110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SIRT4 通过线粒体损伤发挥其在神经母细胞瘤中的肿瘤抑制作用
Authors Wang Y, Guo Y, Gao J, Yuan X
Received 27 April 2018
Accepted for publication 30 June 2018
Published 9 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 5591—5603
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S172509
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: SIRT4 is a member of the sirtuin family of nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide-dependent enzymes located in the mitochondria, and is involved in
regulating energy metabolism, stress response, and cellular lifespan in
mammalian cells. However, its function in human neuroblastoma (NB) remains
unexplored.
Methods: Expression of SIRT4 in 158 pairs of human NB tumor tissues and
adjacent normal tissues collected from March 2009 to October 2012 was analyzed
by immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and real-time fluorescence
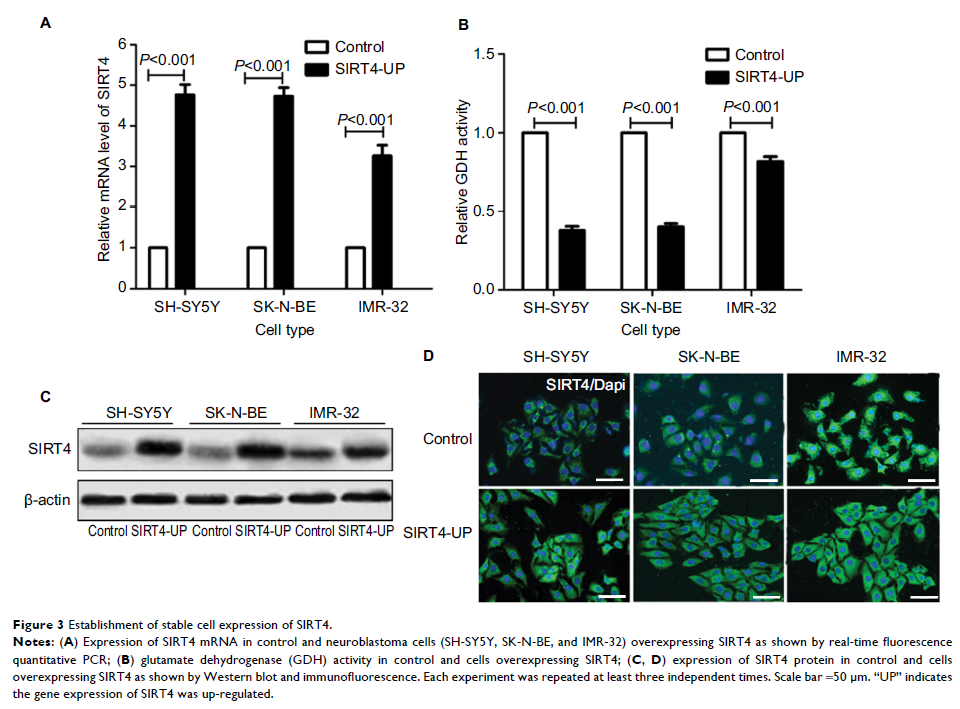
quantitative PCR. For in vitro study, SIRT4 was overexpressed in SH-SY5Y,
SK-N-BE, and IMR-32 cells to study the effects of SIRT4 expression on
proliferation, invasion, and migration of human NB cells and on mitochondrial
function.
Results: SIRT4 gene expression in human NB tumor tissues was significantly
lower than that in adjacent normal tissues (P <0.001). SIRT4
expression was lower in NB patients with higher International Neuroblastoma
Staging System stage (P =0.018), with
lymph node metastasis, than patients without lymph node metastasis (P <0.001). Survival times of NB
patients with low expression of SIRT4 were significantly shorter than those of
patients with high expression of SIRT4 (P =0.0036).
Overexpression of SIRT4 significantly reduced the proliferation, invasion, and
migration ability of NB cells as well as mitochondrial energy production, and
caused SIRT1 upregulation and mitochondrial damage in NB cells.
Conclusion: SIRT4 exhibits a tumor suppressor function in human NB and
inhibits mitochondrial metabolism and SIRT1 expression in tumor cells, thereby
reducing the energy metabolism of tumor cells. These results suggest that SIRT4
may be a new therapeutic target for human NB.
Keywords: neuroblastoma, SIRT4, energy metabolism, SIRT1