110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用碱处理的丝素蛋白增强磷酸钙骨水泥
Authors Hu M, He Z, Han F, Shi C, Zhou P, Ling F, Zhu X, Yang H, Li B
Received 2 May 2018
Accepted for publication 2 August 2018
Published 9 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7183—7193
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S172881
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Bone cement plays an important role in the treatment of
osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Calcium phosphate cement (CPC) is
a potential alternative to poly(methyl methacrylate), currently the gold
standard of bone cements. However, the poor mechanical properties of CPCs limit
their clinical applications. The objective of this study was to develop
reinforced CPCs for minimally invasive orthopedic surgeries by compositing silk
fibroin (SF) with α-tricalcium phosphate.
Methods: SF solution was treated with calcium hydroxide and characterized
by Zeta potential analyzer and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The
alkaline-treated SF (tSF) was composited with α-tricalcium phosphate to obtain
tSF/CPC composite, which was characterized using mechanical tests, scanning
electron microscopy, handling property and biocompatibility tests, and sheep
vertebral augmentation tests.
Results: Upon treatment with calcium hydroxide, larger SF particles and
more abundant negative charge appeared in tSF solution. The tSF/CPCs exhibited
a compact structure, which consisted of numerous SF -CPC clusters and
needle-like hydroxyapatite (HAp) crystals. In addition, high transition rate of
HAp in tSF/CPCs was achieved. As a result, the mechanical property of tSF/CPC
composite cements was enhanced remarkably, with the compressive strength
reaching as high as 56.3±1.1 MPa. Moreover, the tSF/CPC cements showed good
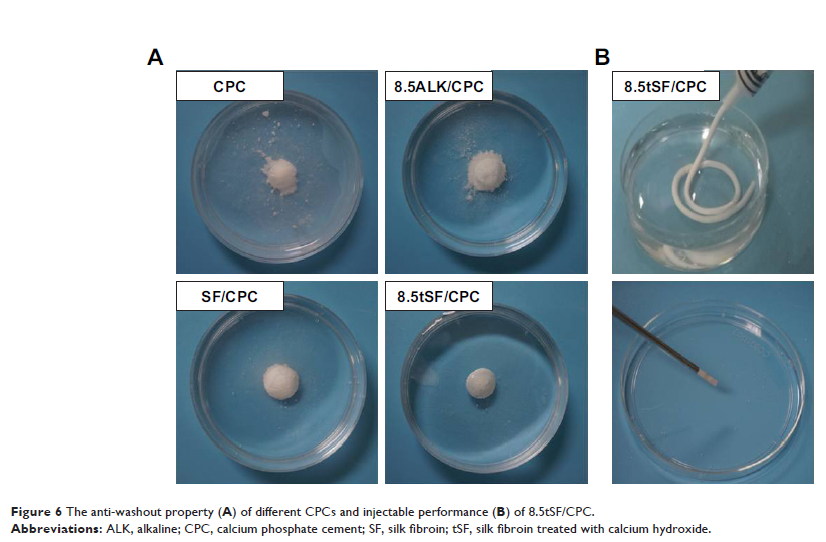
injectability, anti-washout property, and decent biocompatibility. The tSF/CPCs
could be used to augment defected sheep vertebrae to restore their mechanical
strength.
Conclusion: tSF/CPC may be a promising composite bone cement for minimally
invasive orthopedic surgeries.
Keywords: bone cement, silk fibroin, calcium phosphate, calcium hydroxide,
reinforcement