110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胃癌 D2 淋巴结切除术后区域淋巴结复发的模式:重新思考目标量
Authors Yang W, Zhou M, Hu R, Li G, Wang Y, Shen L, Liang L, Yang J, Zhang Z
Received 15 June 2018
Accepted for publication 16 October 2018
Published 12 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8015—8024
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S177315
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: This
study mapped the localization of regional nodal recurrence to determine whether
the clinical target volume (CTV) should be redefined in adjuvant radiotherapy.
Patients and methods: Between January
2004 and October 2015, a total of 129 patients with gastric cancer following D2
resection who experienced regional recurrence were retrospectively examined.
The lymph nodes (LNs) were hand-drawn proportionally on template computed
tomography (CT) images of a standard patient by referencing surrounding
anatomic landmarks. The association between clinicopathologic factors and LNs
at risk was further investigated.
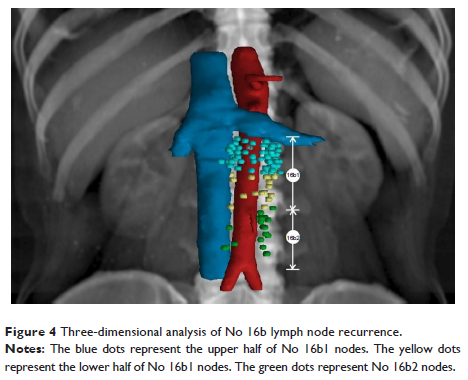
Results: Based on the contour
of the recurrent LNs, the authors observed high-risk regions for relapse and
drew a density distribution map of 16 LN stations on the CT images. The most
commonly involved recurrent LNs were stations 16b (51.2%) and 16a (39.5%).
Stations 13, 12, 9, and 14 were involved in 36.4%, 33.3%, 28.7%, and 27.9% of
recurrences, respectively. Other regions, including stations 1–6 (perigastric
LNs) and station 10 (splenic hilar LN), were of low risk. Notably, 72% (83/116)
of recurrent 16b LNs were located in the upper half of 16b1. Analysis within
subgroups showed that the pathologic N stage was the only independent risk
factor for LN 16 relapse.
Conclusion: This mapping
suggests a new method for vessel-guided delineation of regional LNs when
defining the CTV in patients after standard D2 resection. LNs around the
abdominal aorta and its main branches, as well as regions around the hepatic
hilar area and pancreatic head, should be the most important radiotherapeutic
targets.
Keywords: gastric
cancer, regional, lymph nodes, recurrence, target volume