110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CLIC1 作为口腔鳞状细胞癌潜在生物标志物的表达:一项初步研究
Authors Xu Y, Xu J, Feng J, Li J, Jiang C, Li X, Zou S, Wang Q, Li Y
Received 1 August 2018
Accepted for publication 5 October 2018
Published 12 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8073—8081
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S181936
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Purpose: CLIC1, a
member of the highly conserved class ion-channel protein family, is frequently
upregulated in multiple human malignancies and has been demonstrated to play a
critical role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. However, limited
is known about its expression, biological functions, and action mechanism in
oral malignancies. We aimed to evaluate whether CLIC1 could be a biomarker for
oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods: Immunohistochemistry
was used to analyze the expression of CLIC1 in tissue. CLIC1 protein and mRNA
were measured through Western immunoblotting and quantitative real-time PCR.
CLIC1 protein expression in plasma was detected via ELISA. A total of 72 OSCC
specimens were recruited in this study for evaluation of correlations of CLIC1
with clinicopathological features and survival.
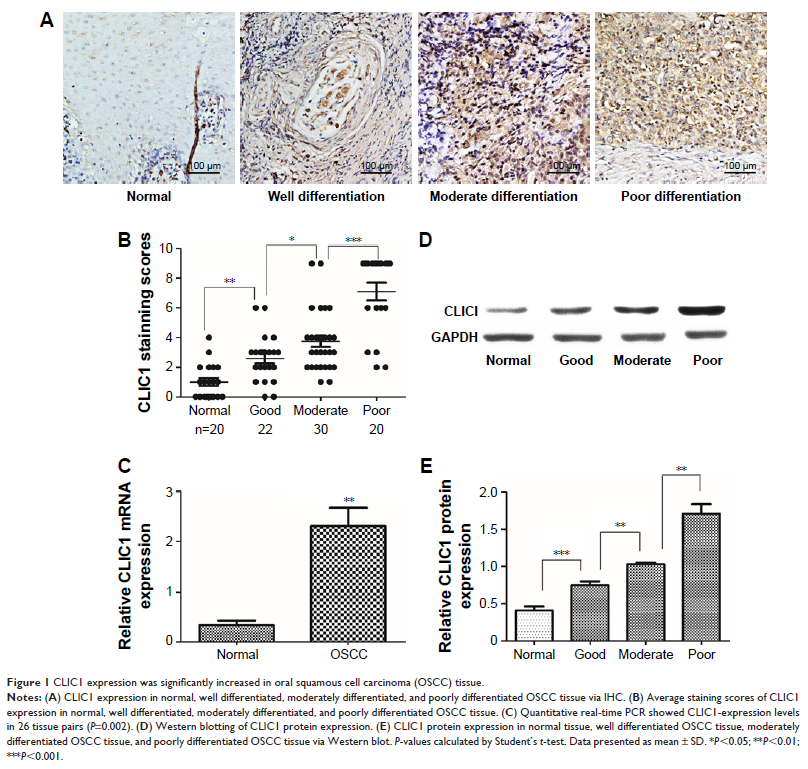
Results: CLIC1 was
significantly overexpressed in tissue and plasma of OSCC patients. It was found
that upregulated CLIC1 was distinctly correlated with histological grade, TNM
stage, and tumor size. Meanwhile, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that
OSCC patients with high CLIC1 expression had remarkably poorer overall survival
rate than those with low CLIC1 expression. Multivariate Cox regression analysis
revealed that CLIC1 was the independent prognostic factor for overall survival
rate of OSCC patients. In addition, Pearson correlation analysis showed that
CLIC1 was associated with multiple tumor-associated genes.
Conclusion: These results
indicated that CLIC1 acts as a molecular target in OSCC and may present a novel
diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for OSCC.
Keywords: chloride
intracellular channel 1, oral squamous cell carcinoma, expression, prognosis,
biomarker