110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小檗胺对头颈部鳞状细胞癌的体外和体内出色的放射增敏作用
Authors Zhu H, Ruan S, Jia F, Chu J, Zhu Y, Huang Y, Liu G
Received 15 April 2018
Accepted for publication 20 July 2018
Published 14 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8117—8125
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S171212
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Berbamine
(BBM), one of the bis-benzylisoquinoline products isolated from Berberis amurensis,
has been demonstrated for its anticancer effect against leukemia, breast
cancer, liver cancer, etc. There are some studies focusing on the
chemosensitization effect of BBM. However, there is no report about whether BBM
could enhance the anticancer effect of radiation, which made us to explore the
possible radiosensitization effect of BBM.
Materials and methods: Here, in
vitro cytotoxicity of BBM was evaluated on two kinds of head and neck squamous
cancer cell lines. Clonogenic assay was performed to study the
radiosensitization effect of BBM. Western blot was utilized to elucidate the
possible mechanism underlying the radiosensitization effect.
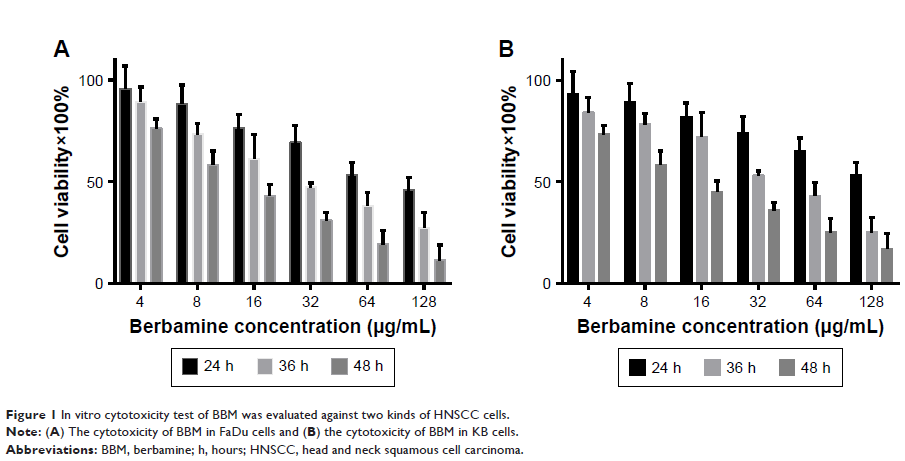
Results: BBM
effectively inhibited the growth of two kinds of cancer cells in a time- and
dose-dependent manner. Radiation plus BBM led to significantly more reduction
of the colony-forming ability of cancer cells when compared with radiation
alone. BBM plus radiation led to the most reduction of STAT3 phosphorylation,
followed by the significant decrease of the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2. In vivo study
demonstrated that the combinational administration of BBM and radiation
generated the most significant tumor-delaying effect among all of the treatment
regimens.
Conclusion: We
reported, in the current study, the potential role of BBM in not only treating
cancer by itself but also offering a promising way to improve the efficacy of
radiotherapy by inhibiting the activation of STAT3 and subsequently inducing
the apoptosis of cancer.
Keywords: berbamine,
radiation, HNSCC, sensitization