110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

硫酸钙水泥多孔 TiO2 微球复合材料的控释和持续释药性能
Authors Luo W, Geng Z, Li Z, Wu S, Cui Z, Zhu S, Liang Y, Yang X
Received 20 June 2018
Accepted for publication 3 October 2018
Published 14 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7491—7501
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S177784
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Calcium
sulphate cement (CSC) is widely used as an osteoconductive biomaterial in bone
repair and regeneration.
Purpose: In this
study, porous TiO2 microspheres
were added to CSC to achieve a controlled and sustained drug (gentamicin)
release.
Methods: Scanning
electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray powder
diffraction (XRD), and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area analysis were
conducted to analyse the morphology, phase composition, and surface area of the
TiO2 microspheres and composite cements. In
addition, the injection time, compressive strength, degradation behaviour, and
antibacterial ability of the composite cements were examined during in vitro
degradation. Gentamicin release profile was recorded using an ultraviolet
spectrophotometer.
Results: The
results revealed the excellent drug loading ability of the TiO2 microspheres.
The addition of TiO2 microspheres improved the injectability
and compressive strength of the composite cements, the maximum value of which
was achieved at a TiO2 loading of 5 wt.%. When immersed in
simulated body fluid (SBF), the composite cements doped with TiO2 microspheres
were observed to release gentamicin in a stable and sustained manner,
especially in the latter stages of in vitro degradation. During degradation,
CSC doped with TiO2 microspheres exhibited a typical
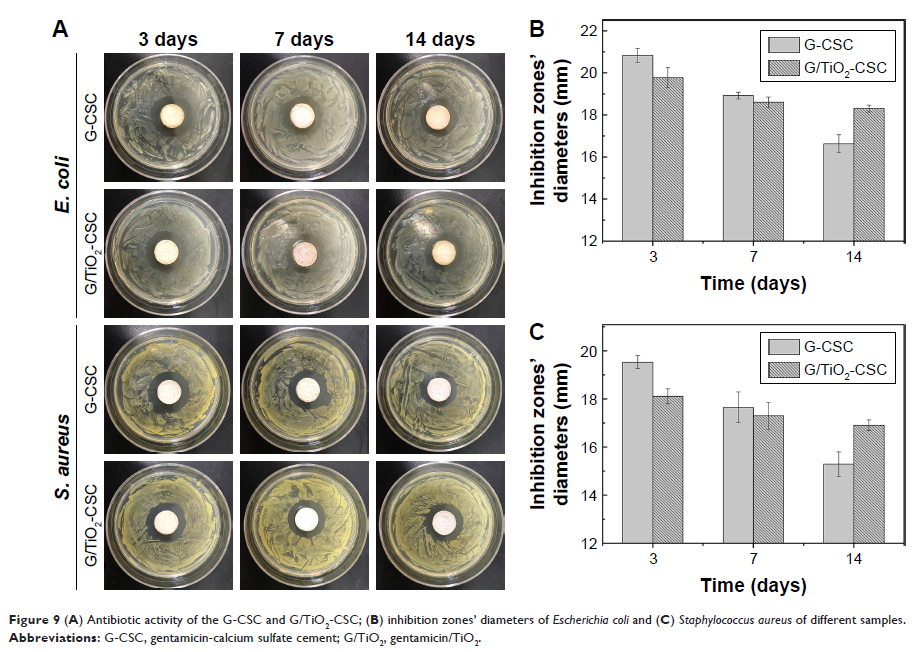
apatite-like behaviour. Further, antibacterial analysis showed that CSC doped
with TiO2 microspheres exhibited long-term
antibiotic activity.
Conclusion: Thus, as
an effective sustained-release formulation material, TiO2 microspheres
show a great potential for application in bone cements.
Keywords: TiO2, microsphere,
calcium sulfate cement, sustained drug release, antibacterial ability