110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

A666-缀合的纳米颗粒可靶向外毛细胞的动力蛋白,防止顺铂诱导的听力丧失
Authors Wang XL, Chen YM, Tao Y, Gao YG, Yu DH, Wu H
Received 4 April 2018
Accepted for publication 28 June 2018
Published 14 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7517—7531
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S170130
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: The
delivery of treatment agents to inner ear with drug delivery system (DDS) has
been under investigation to overcome the limitations of the conventional
therapeutic agents in curing or alleviating the cisplatin ototoxicity.
Methods: In the
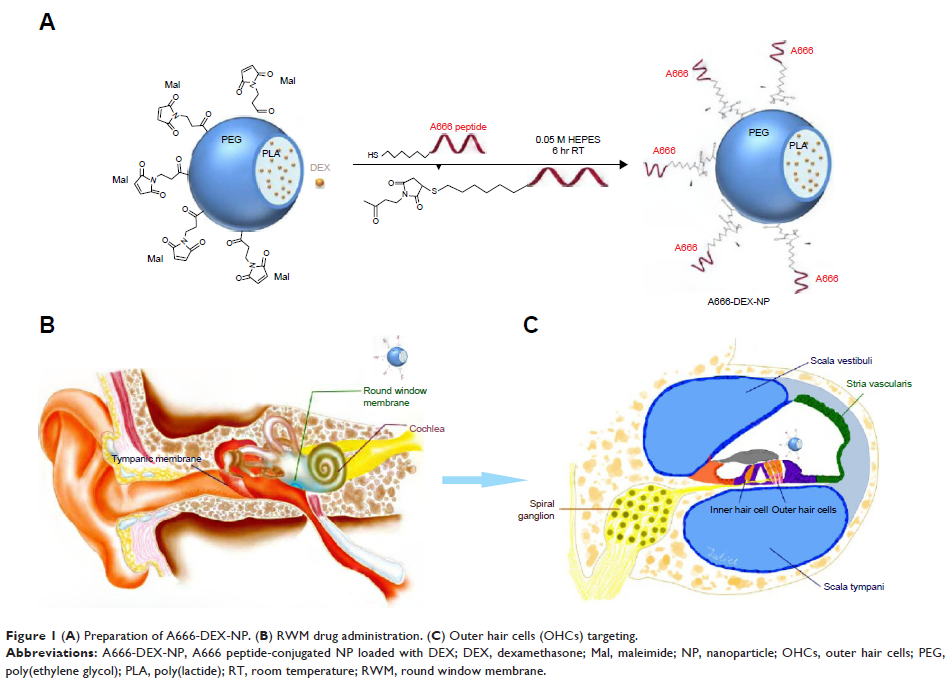
present study, a novel targeted dexamethasone (DEX)-loaded DDS, A666-DEX-NP,
was constructed for prevention from cisplatin-induced hearing loss.
A666-(CLEPRWGFGWWLH) peptides specifically bind to prestin, which is limited to
the outer hair cells (OHCs). HEI-OC1 and cisplatin-treated guinea pigs (12
mg/kg, intraperitoneal) were used as in vitro and in vivo models for
investigating the targeting and protective efficiency against cisplatin.
Results: As
expected, compared to A666-unconjugated nanoparticles (NP), A666-conjugated
coumarin 6-labeled NP showed active targeting to OHCs. Furthermore,
A666-coumarin 6-labeled NP could be significantly internalized by HEI-OC1 cells
via the A666–prestin interaction. This facilitated the uptake of cells
pretreated with A666-DEX-NP, followed by the cisplatin-treated group, which led
to enhanced cell viability, reduced apoptotic properties, and decreased
reactive oxygen species levels as compared to cells pretreated with DEX or
DEX-NP, 4 hours in advance of cisplatin treatment. In cisplatin-treated guinea
pigs, pretreatment with A666-DEX-NP effectively preserved OHCs and showed
significant hearing protection at 4, 8, and 16 kHz as compared to pretreatment
with saline, DEX, or DEX-NP formulation.
Conclusion: This
OHC-targeting DDS provides a novel strategy for DEX application that can be
potentially used to combat cisplatin ototoxicity.
Keywords: A666
peptide, dexamethasone, prestin, cisplatin ototoxicity