110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

鉴定和验证 4-miRNA(miRNA-21-5p,miRNA-9-5p,miR-149-5p 和 miRNA-30b-5p)在透明细胞肾细胞癌中的预后特征
Authors Xie MZ, Lv YF, Liu ZH, Zhang JY, Liang CY, Liao XL, Liang R, Lin Y, Li YQ
Received 11 September 2018
Accepted for publication 11 October 2018
Published 15 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 5759—5766
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187109
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: Clear cell
renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is one of the most common cancers with high
mortality worldwide. However, biomarkers for predicting prognosis in ccRCC are
limited. In this study, we attempted to identify potential prognostic
biomarkers of ccRCC.
Methods: Clinical
information and the preprocessed ccRCC mature miRNA expression profiles in The
Cancer Genome Atlas database were downloaded from UCSC Xena. The miRNAs
differentially expressed between ccRCCs and matched normal tissues were
analyzed using the “limma” package. A miRNA-based signature was constructed
using the multivariate Cox regression model with prognosis index (PI) formula.
Patients with ccRCC were divided into low-risk and high-risk subgroups
according to median PI. The survival times were compared between the two groups
using Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test. The training set was used to
construct a miRNA-based signature for predicting prognosis. The test set was
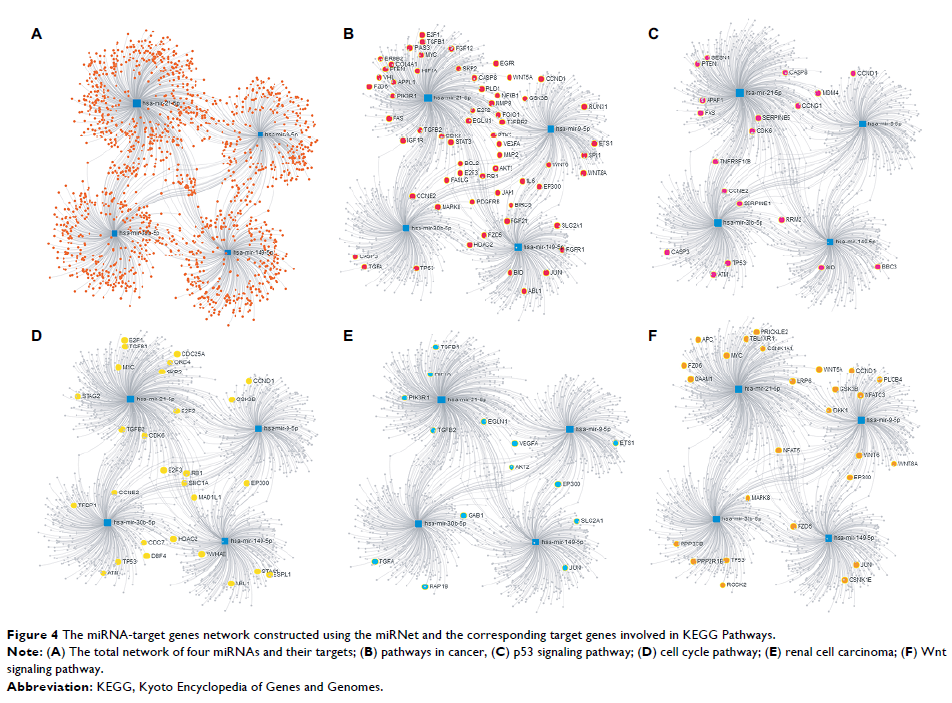
used to verify the signature. Target gene prediction and functional enrichment
analysis of the four miRNAs were performed using miRNet.
Results: We identified
four miRNAs, miRNA-21-5p, miRNA-9-5p, miR-149-5p, and miRNA-30b-5p, as
independent prognostic indicators. Next, we used these four miRNAs to construct
a four-miRNA PI for each patient. Results revealed that patients in the
high-risk group (n=119) had significantly shorter survival time than those in
the low-risk group (n=118) (high-risk/low-risk group log-rank P =0.000). This
four-miRNA signature is an independent prognostic factor compared with routine
clinicopathological features in the test set. These miRNAs targeted 1,634
genes, and a miRNA-target gene network was constructed using miRNet. The target
genes of these four miRNAs were involved in various pathways related to cancer.
Conclusion: Our observations
suggest that the four-miRNA signature correlated with the survival of patients
with ccRCC and can be used as a prognostic biomarker of ccRCC.
Keywords: ccRCC, miRNA
signature, overall survival, prognostic biomarkers