110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

加载蟾蜍灵的维生素E琥珀酸酯-接枝 - 壳聚糖寡糖/RGD 结合的 TPGS 混合胶束具有针对抗药性结肠癌的抗肿瘤活性
Authors Yuan Z, Yuan Y, Han L, Qiu Y, Huang X, Gao F, Fan G, Zhang Y, Tang X, He X, Xu K, Yin P
Received 10 April 2018
Accepted for publication 9 August 2018
Published 15 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7533—7548
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S170692
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Multidrug
resistance (MDR) is the major reason for the failure of chemotherapy in colon
cancer. Bufalin (BU) is one of the most effective antitumor active constituents
in Chansu. Our previous study found that BU can effectively reverse
P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated MDR in colon cancer. However, the clinical
application of BU is limited due to its low solubility in water and high
toxicity. In the present study, a multifunctional delivery system based on
vitamin-E-succinate grafted chitosan oligosaccharide (VES-CSO) and cyclic
(arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide) (RGD)-modified d-alpha-tocopheryl
polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was prepared by emulsion solvent
evaporation method for targeted delivery of BU to improve the efficacy of
drug-resistant colon cancer therapy.
Methods: The
cytotoxicity of BU-loaded micelles against drug-resistant colon cancer LoVo/ADR
and HCT116/LOHP cells was measured by CCK-8 assay. The cellular uptake, Rho123
accumulation, and cell apoptosis were determined by flow cytometry. The
expression of apoptosis-related protein and P-gp was measured by Western blot
assay. The antitumor activity of BU-loaded micelles was evaluated in
LoVo/ADR-bearing nude mice.
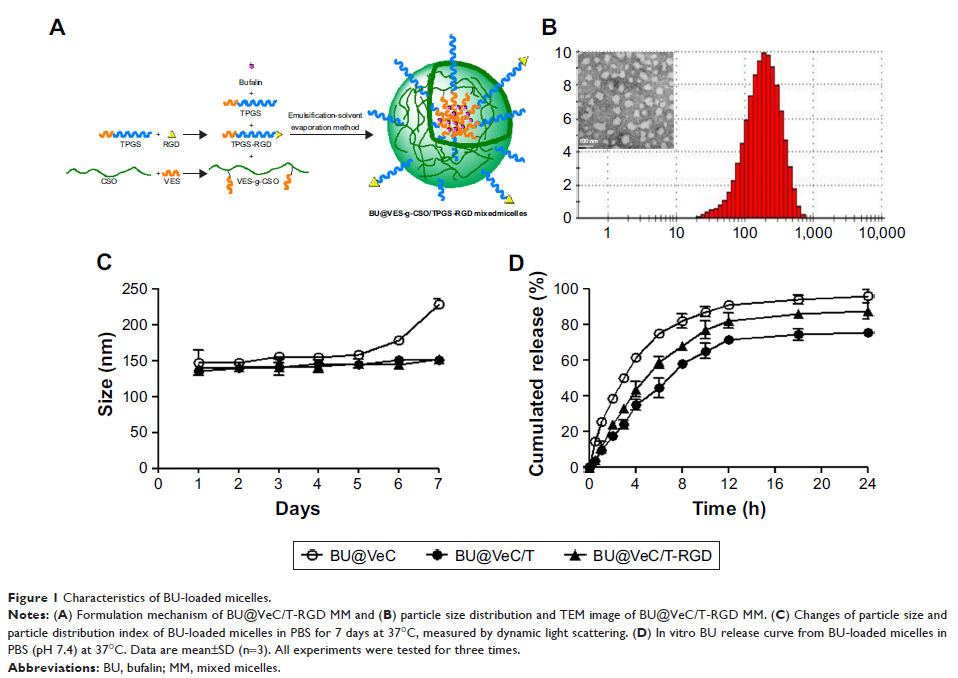
Results: BU-loaded
VES-CSO/TPGS-RGD mixed micelles (BU@VeC/T-RGD MM) were 140.3 nm in diameter
with zeta potential of 8.66 mV. The BU@VeC/T-RGD MM exhibited good stability,
sustained-release pattern, higher intracellular uptake, and greater
cytotoxicity in LoVo/ADR cells. Furthermore, the mechanisms of the BU@VeC/T-RGD
MM to overcome MDR might be due to enhanced apoptosis rate and P-gp efflux
inhibition. Subsequently, in vivo studies confirmed an enhanced therapeutic
efficiency and reduced side effects associated with BU@VeC/T-RGD MM compared
with free BU, owing to the enhanced permeation and retention effect, improved
pharmacokinetic behavior, and tumor targeting, which lead to MDR-inhibiting
effect in LoVo/ADR-bearing nude mice.
Conclusion: Our
results demonstrated that VeC/T-RGD MM could be developed as a potential
delivery system for BU to improve its antitumor activity against drug-resistant
colon cancer.
Keywords: bufalin,
colon cancer, multidrug resistance, mixed micelle, tumor targeting, P-gp