110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对中国福建省女性高危型人乳头瘤病毒进行 Cervista® 检测的临床验证:一个横断面研究
Authors Mao X, Ruan G, Dong B, Chen L, Xu S, Lin F, Sun P
Received 6 July 2018
Accepted for publication 17 October 2018
Published 16 November 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 2243—2253
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S179334
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Purpose: To
estimate the high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) prevalence in a
hospital-based population using the Cervista® and to
determine the clinical value and significance of Cervista for cervical cancer
screening in Fujian Province, China.
Patients and methods: In a
hospital-based population, a total of 10,771 women from the Fujian Province
were screened for cervical cancer and precancerous lesions using the thinprep
cytologic test (TCT) and/or the Cervista. Women with HR-HPV infection and/or
abnormal TCT were referred for colposcopy and biopsy. Pathological diagnosis
was used as the gold standard.
Results: The
overall HR-HPV prevalence was 16.57%. Among 10,229 cases, 976 had abnormal
cytology results, of which, the HR-HPV positivity rate was 60.35% in this
opportunistic screening population. The most common HR-HPV infection style was
a simple infection. The most common species was A9 which was also the most
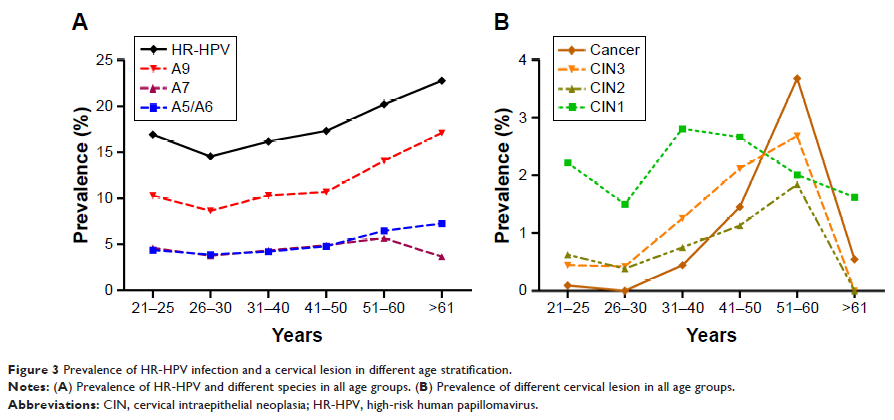
prevalent species in all age. The women with CIN2+ (high-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesion [HSIL]), especially cancer, were mostly concentrated in
the age from 51 to 60 years old. The peak of CIN1 (low-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesion, LSIL) prevalence was in the women aged 31–40. When
using CIN1+, CIN2+ and CIN3+ as observed endpoints, the sensitivities were
86.07%, 92.73%, and 93.30% and negative likelihood ratio (NPV) were 99.15%,
99.75% and 99.83%, respectively. Cervista and TCT co-testing achieved the
highest sensitivity and the lowest NLR.
Conclusion: The
Cervista could be easily introduced in clinical practice in combination with
TCT for cervical cancer screening in China. Patients with species A9 infection
require a more actively clinical intervention.
Keywords: high-risk
human papillomavirus, Cervista®, cytology, pathological diagnosis, cervical
cancer