110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国急性冠状动脉综合征患者不受控制的高血脂:一个观察性研究
Authors Jiang J, Zhou YJ, Li JJ, Ge JB, Feng YQ, Huo Y
Received 26 June 2018
Accepted for publication 16 October 2018
Published 16 November 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 2255—2264
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S178318
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: Despite
current standard of care, the overall lipid goal attainment rate for
hyperlipidemia patients, especially those who have experienced acute coronary
syndrome (ACS), is suboptimal, which predisposes them to a higher residual risk
of atherothrombotic events. This study aimed to describe characteristics of
Chinese patients who recently experienced an ACS event and were on
lipid-lowering treatment, yet failing to reach targeted goal.
Methods: A
multicenter, cross-sectional study was conducted to recruit 2,034 Chinese
patients who experienced an ACS (ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
[STEMI], non-STEMI, or unstable angina) event within the past 4–40 weeks and
were on statin treatment (>2 weeks) from March 2015 to December 2016. All
eligible patients underwent a fasting lipid test after enrollment and data on
medical history were collected.
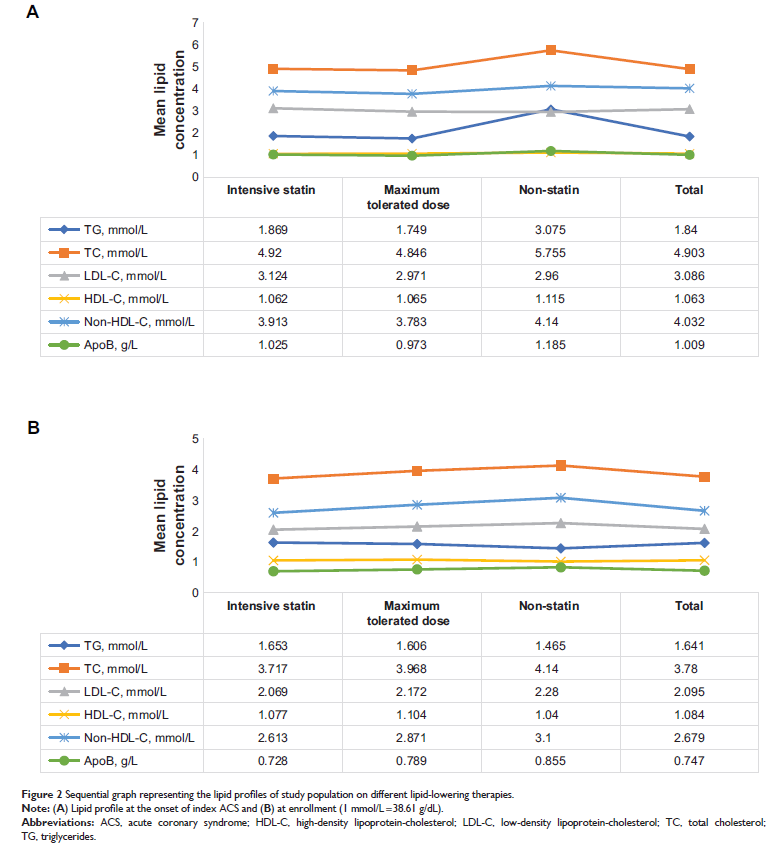
Results: The mean
age of 1,994 eligible patients was 61.0±9.84 years. Among them, 1,493 (74.9%)
patients received intensive statin therapy (defined as atorvastatin 40 or 80
mg, or rosuvastatin 20 mg per protocol) and 499 (25.0%) patients were on
maximum tolerated dose statin. Of the 1,994 eligible subjects, 1,273 (63.8%)
patients did not achieve the lipid goal at the time of enrollment. Among the
not-at-goal patients, 910 (71.5%) received intensive statin therapy; the
majority (73.4%) of them were male; the mean age was 61.2±10.1 years old; 699
(54.9%) patients had a history of hypertension; 25.3% had diabetes mellitus;
and 29.5% were current smokers. The mean low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
(LDL-C), non-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (non-HDL-C), and ApoB levels
at enrollment of this group of patients were 2.460±0.7139 mmol/L, 3.094±0.8861
mmol/L, and 0.840±0.3015 g/L, respectively.
Conclusion: The study
result demonstrates that overall more than half of the patients who recently
(4–40 weeks) experienced ACS who were treated did not reach the
guideline-recommended LDL-C and non-HDL-C goal. These results highlight the
potential necessity for a new drug beyond statins to further reduce disease
burden in the future.
Keywords: acute
coronary syndrome, intensive statin treatment, lipid goal attainment,
lipid-lowering treatment