110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过定向方式抑制由 ROS 介导的激活 Src-MAPK/AKT 信号来减轻 H2O2 诱导下的 PC12 细胞凋亡
Authors Qi S, Feng Z, Li Q, Qi Z, Zhang Y
Received 25 June 2018
Accepted for publication 17 October 2018
Published 16 November 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3973—3984
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S178217
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: Reactive
oxygen species (ROS) are considered a direct cause of neurodegenerative
diseases (NDDs). Drugs developed to target ROS are effective for the treatment
of NDDs. Orientin is a pyrone glucoside extracted from Polygonum orientale ,
and it exhibits many pharmacological activities. In this study, we aimed to
determine whether orientin could relieve hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced
neuronal apoptosis and to investigate the specific target of orientin.
Materials and methods: In this study,
the neuroprotective effect and its possible mechanisms of orientin in mouse
pheochromocytoma cell line (PC12) cells stimulated by H2O2, establishing
an oxidative stress model, were investigated. And we further tested the role of
ROS in the neuroprotective effects of orientin.
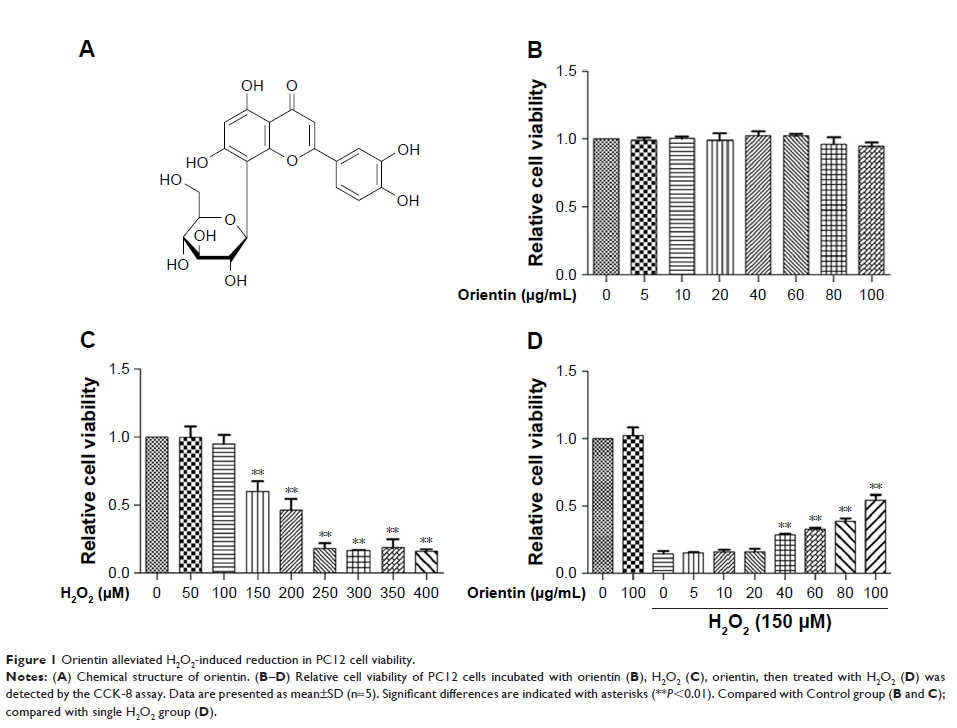
Results: Orientin
(5–100 µg/mL) did not cause toxicity in PC12 cells but significantly decreased
H2O2-induced reduction in PC12 cell viability, cell
apoptosis rates, and nuclear condensation. It also inhibited the activation of
caspase-3 and degradation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Under the
stimulation of H2O2, MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38), AKT, and Src
signaling proteins in PC12 cells were activated in a time-dependent manner. The
application of inhibitors that were specific for MAPKs, AKT, and Src
effectively alleviated H2O2-induced cell apoptosis. In addition, the Src
inhibitor decreased the activation of MAPKs and AKT signaling. More
importantly, orientin effectively decreased H2O2-induced
phosphorylation of MAPKs, AKT, and Src signaling proteins. Finally, we
confirmed that orientin effectively inhibited H2O2-induced
accumulation of ROS in cells. In addition, ROS inhibitors blocked the
Src-MAPKs/AKT signaling pathway-dependent cell apoptosis stimulated by H2O2.
Conclusion: These results
indicate that alleviation of H2O2-induced cell apoptosis by orientin is Src-MAPKs/AKT
dependent. Overall, our study confirms that orientin alleviates H2O2-induced cell
apoptosis by inhibiting the ROS-mediated activation of Src-MAPKs/AKT signaling.
Keywords: oxidative
stress, orientin, neuroprotection, apoptosis, Src, MAPKs, AKT