110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

整联蛋白和肝素敏感分子调节下的最初成骨细胞粘附及随后在氧化锆表面上的分化
Authors Luo F, Hong G, Matsui H, Endo K, Wan Q, Sasaki K
Received 28 May 2018
Accepted for publication 27 August 2018
Published 19 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7657—7667
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S175536
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: It is
well known that zirconia materials have good biocompatibility; however, little
is known regarding the mechanism by which cells attach to these materials. The
purpose of this study is to elucidate the mechanism of cell attachment.
Materials and methods: In this
study, we examined the surface characteristics of ceria-stabilized
zirconia/alumina nanocomposite (NANOZR), yttria-stabilized zirconia (Y-TZP) and
commercially pure titanium (CpTi), and we evaluated the initial response of
osteoblast-like cells to them with different inhibitors.
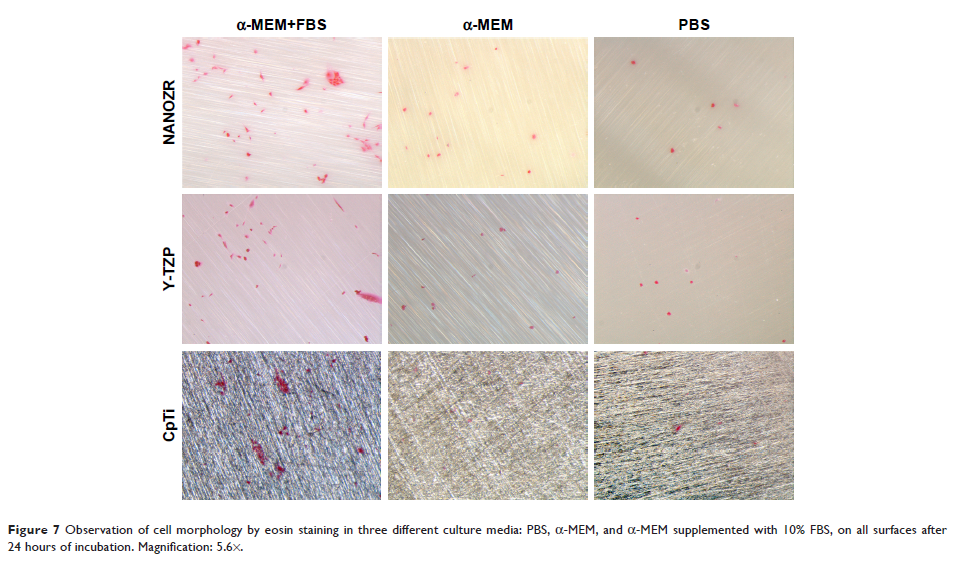
Results: Under the
same polishing treatment, the three materials, NANOZR, Y-TZP and CpTi, show
similar surface wettability but different surface roughness. Osteoblasts could
adhere to the surface of all three materials, and spindle shapes were clearer
in serum-containing media compared to PBS and serum-free culture media,
suggesting that serum-contained proteins are helpful for the initial cell
adhesion and spreading. Cell adhesion and proliferation were disrupted in the
presence of EDTA. RGD-peptide interfered with cell proliferation by affecting
cell protrusion and stress fibers. Monoclonal antibody against non-RGD type
integrin α2β1 enhanced proliferation in Y-TZP, CpTi and
culture dish but not in NANOZR. Cell proliferation on NANOZR was specifically
inhibited in the presence of heparin. Furthermore, under heparin
administration, spindle shape formation was maintained but actin cytoskeleton
was disrupted, resulting in loose cellular spreading.
Conclusion: These
results suggest that RGD type integrins and heparin-sensitive protein in
coordination regulate cell morphology and proliferation on NANOZR, through the
regulation of cell polarity and stress fiber formation, respectively.
Keywords: zirconia,
biocompatibility, adhesion, RGD-peptide, integrins