110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

二氧化硅纳米粒子和醋酸铅对心血管系统的共同亚急性毒性
Authors Feng L, Yang X, Shi Y, Liang S, Zhao T, Duan J, Sun Z
Received 24 August 2018
Accepted for publication 26 September 2018
Published 21 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7819—7834
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S185259
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: The harmful effects following the release
of nanomaterials into environment are of great concern today.
Purpose: In
this study, subacute effect due to co-exposure to low-dose silica nanoparticles
(SiNPs) and lead acetate (Pb) on cardiovascular system was detected in Sprague
Dawley male rats.
Materials and Methods: Histopathological and ultrastructural changes of
heart, aortic arch and abdominal aorta were detected. Blood routine and blood
biochemistry examinations were used to show the changes of blood components.
The fibrinolytic and plasmin factors, inflammation-related factors and
myocardial-related enzyme in serum were analysised by ELISA and Western blot
assay.
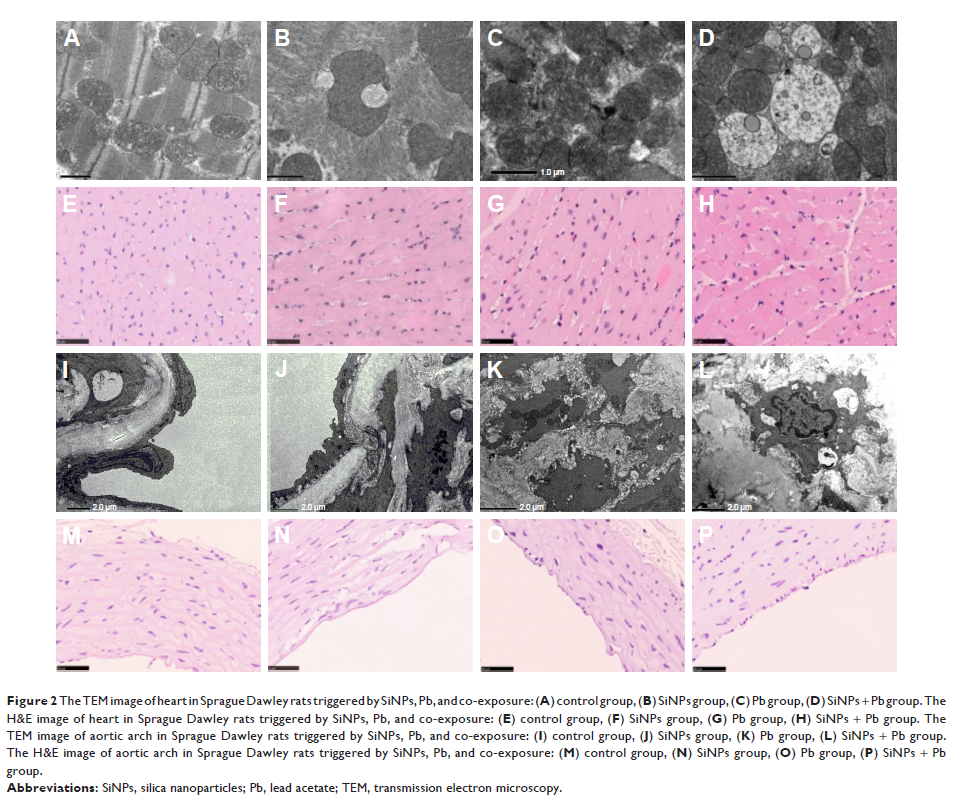
Results: Histopathological
and ultrastructural examination of heart, aortic arch, and abdominal aorta
showed that serious damage occurred in co-exposure group (n=6/group). Blood
routine examination showed that leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia increased
markedly, while changes in the erythrocyte count were not obvious in the
co-exposure group. The expression of alanine transaminase (ALT) decreased
obviously in co-exposure group, while no significant changes were noted in the
expression of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), cholesterol (CHO), triglyceride
(TG), high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density
lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) in the co-exposure group on blood biochemistry
analysis. In addition, data from ELISA analysis showed that the levels of
fibrinolytic and plasmin factors, including thrombin time (TT), prothrombin
time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), tissue-type
plasminogen activator (t-PA), tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), and
antithrombin III (AT III), were decreased, while those of human fibrinogen
(FIB) and D-dimer (D2D) increased significantly in the co-exposure group.
Moreover, the myocardial-related enzyme in serum, tested by ELISA, and
cardiovascular-related protein expression of atrial natriuretic peptide and
brain natriuretic peptide, tested by Western blot assay, was increased in the
heart. Furthermore, the expression of inflammation factors such as C-reactive
protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was
increased in heart tissue subjected to combined exposure, which was manifested
by Western blot assay, while the protein levels of angiotensin II (ANG II) and
endothelin 1 were (ET-1) elevated in blood vessels in the co-exposure group.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the major interactions involved in subacute toxicity due
to co-exposure to low doses of SiNPs and Pb on cardiovascular system were
expected to be additive and synergistic in nature. Co-exposure to SiNPs and Pb
could aggravate the cardiovascular toxicity via endothelial damage,
hypercoagulation, and cardiac injury in vivo.
Keywords: SiNPs,
Pb, combined exposure, cardiovascular toxicity, in vivo