110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在帕金森病中异常表达的长非编码 RNA 和基因
Authors Zhou Y, Gu C, Li J, Zhu L, Huang G, Dai J, Huang H
Received 29 June 2018
Accepted for publication 3 October 2018
Published 22 November 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 3219—3229
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S178435
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: Parkinson’s
disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative movement disorder, but the
pathogenesis remains elusive. This study was aimed to explore key genes and
long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) associated with PD.
Materials and methods: Three
patients with PD and three normal controls were enrolled in the present study
from July 12, 2017, to August 29, 2017. RNA sequencing and bioinformatics
analysis were performed to obtain differentially expressed micro RNAs (DEmRNAs)
and lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) between patients with PD and normal controls.
PD-specific protein–protein interaction networks were constructed. DEmRNAs
transcribed within a 100 kb window upstream or downstream of DElncRNAs
were searched, which were defined as cis nearby targeted DEmRNAs of DElncRNAs.
Datasets GSE57475 and GSE68719 were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus
database, which were used to validate the expression of selected DEmRNAs.
Results: A total of 857
DEmRNAs and 77 DElncRNAs were obtained between PD and normal controls. Natural
killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity was a significantly enriched pathway in PD.
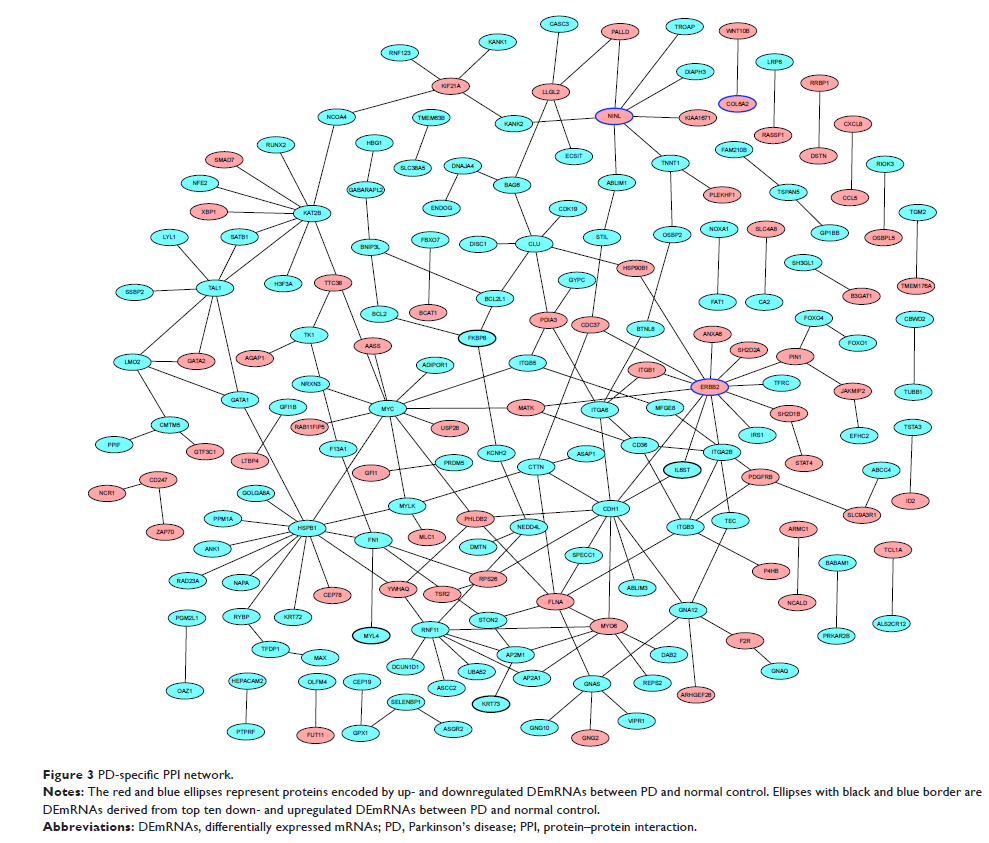
ERBB2, HSPB1, and MYC were three hub proteins of PD-specific protein–protein
interaction network. LOC105378701-TAL1 , LOC102724104-CX3CR1 , LOC105375056-TREML1/TREML4 ,
LOC105379392-ANK1 ,
and LOC101928100-KLRK1/KLRD1 interactions were identified DElncRNA
nearby targeted DEmRNA pairs in PD. Gene expression results validated by
GSE57475 and GSE68719 were consistent with our RNA-sequencing results,
generally.
Conclusion: This
present study identified key genes and lncRNAs associated with PD, which will
provide new clues for exploring the pathogenesis and developing potential biomarkers
of PD.
Keywords: RNA-sequencing,
mRNA, bioinformatics analysis, protein–protein interaction network