110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肝脏手术延长了胃肠道间质瘤肝转移患者的生存期:一个单一中心的回顾性研究
Authors Xiao BY, Peng JH, Tang JH, Zhang RX, Li C, Lin JZ, Ding PR, Wan DS, Pan ZZ, Wu XJ
Received 10 September 2018
Accepted for publication 22 October 2018
Published 22 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6121—6127
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187061
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objectives: Gastrointestinal
stromal tumor (GIST) liver metastasis (GLM) is a special subset of advanced
GIST, because its lesions are easier to define and assess. We aim to determine
the role of liver metastasectomy for patients with GLM in the era of tyrosine
kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy.
Methods: We
reviewed patients with metastatic GIST who received surgery or other treatments
in Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center between January 1991 and December 2017.
Patients with metastases confined to the liver and with no previous metastasis
to other locations were included into the study and were classified into
surgical and non-surgical groups. All patients received 400 mg/d imatinib
after the operation. We compared progression-free survival (PFS) and overall
survival (OS) between the two groups.
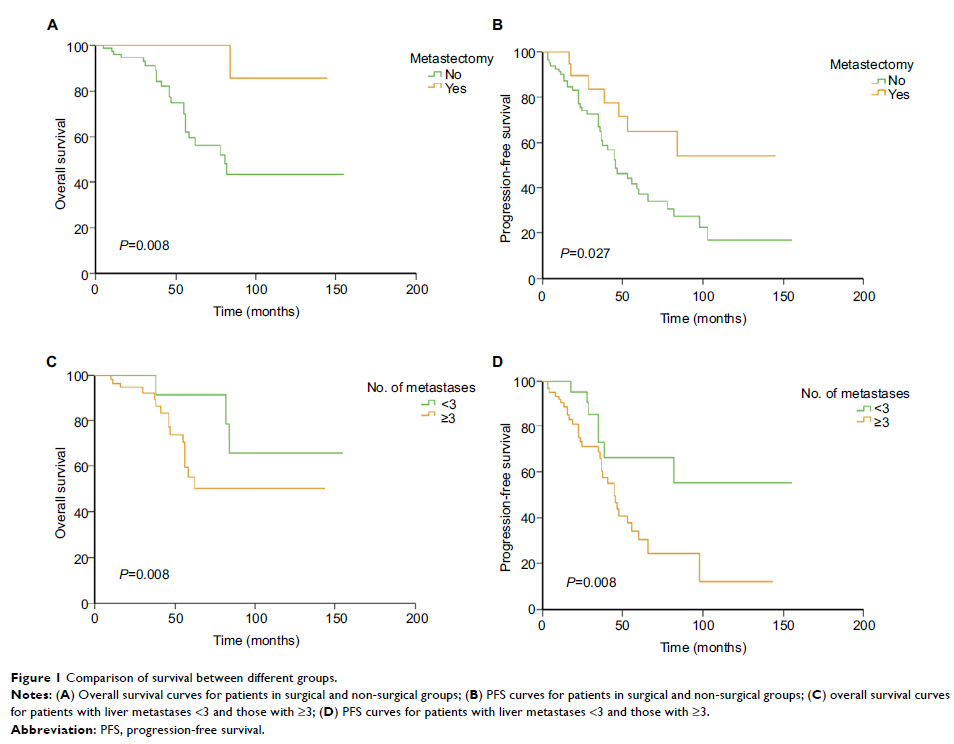
Results: A total
of 102 patients were included into the study. Of them, 21 (20.1%) underwent
surgery for liver metastases and 81 (79.9%) received TKI therapy alone. During
the operation, six patients received radiofrequency ablation for suspicious or
unresectable lesions. Three-year PFS rate was 77.5% in the surgical group and
65.5% in the non-surgical group (P =0.027); 5-year OS rate was 85.7% and 59.6%,
respectively (P =0.008).
About 22.1% of patients had metastases of less than three in the surgical
group, while the rate was 42.9% in the non-surgical group (P =0.011). Patients
with metastases of less than three had longer PFS than those with three or
more, with a 3-year PFS rate of 72.8% and 65.8%, respectively (P =0.019). But their
difference in 5-year OS rate was not significant (91.7% vs 55.3%, P =0.08).
Conclusion: Followed by
continuous TKI therapy, R0 surgery significantly prolongs the survival of
patients with GLM, regardless of the extent of disease or the phase of
metastasis.
Keywords: gastrointestinal
stromal tumor, liver metastasis, surgery, metastasectomy