110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

更改后的表皮型脂肪酸结合蛋白在肝细胞癌中的表达预示着不利的结果
Authors Lu J, Cai S, Pan Y, Yun J
Received 26 July 2018
Accepted for publication 21 October 2018
Published 23 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6275—6284
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S181555
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Objective: Hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) is a rapidly proliferating malignancy that requires large
amounts of fatty acids to synthesize cellular membranes and provide energy.
Epidermal fatty acid-binding protein (EFABP) is uniquely expressed in epidermal
cells, but its role and expression in HCC are not clear.
Subjects and methods: A total
of 804 HCC specimens were collected to construct a tissue microarray (TMA) and
for immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis. The relationship between EFABP
expression and clinical features of patients with HCC was analyzed.
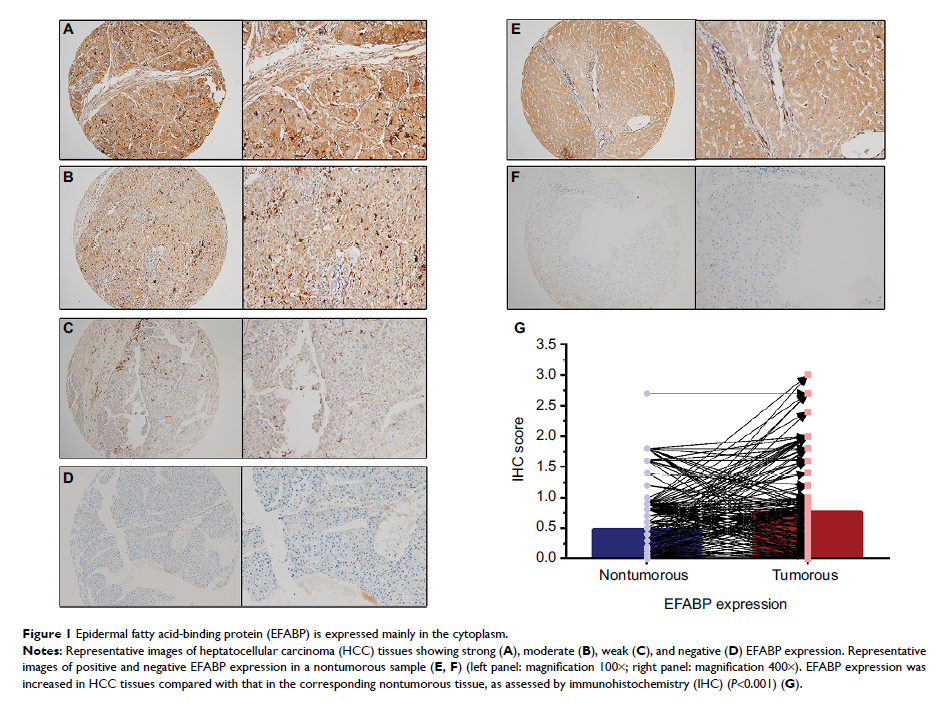
Results: The EFABP
IHC score for HCC tissue was 0.76±0.69, being significantly higher than that
for matched nontumorous tissue (0.48±0.55; P <0.001). Using
the median IHC score (ie, 0.8) in the tumorous tissue, a high level of EFABP
expression was found in 57.3% (461/804) of the cases. Patients with HCC
displaying high EFABP expression had poorer tumor differentiation (P =0.029), more
vascular invasion (P =0.006), and a higher proportion of late TNM stage
disease (P =0.042).
Kaplan–Meier analysis revealed that the patients with high EFABP expression had
significantly worse outcomes in terms of overall survival (P =0.003), worse
disease-free survival (P =0.021), and a higher probability of recurrence (P =0.014).
Multivariate analysis indicated that EFABP expression was an independent
prognostic variable for overall survival (P =0.021) and disease-free survival (P =0.044). For HCC
recurrence, only vascular invasion (P =0.020) and EFABP expression (P =0.026) were
independent risk factors.
Conclusion: Our data
revealed that EFABP expression was increased in HCC samples. High EFABP
expression was correlated with shorter survival times in patients with HCC and
served as an independent factor for worse outcomes. Our study therefore
provides a promising biomarker for the prognostic prediction of HCC and a
potential therapeutic target for the disease.
Keywords: epidermal
fatty acid-binding protein, lipid metabolism, hepatocellular carcinoma,
prognostic biomarker