110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FAM129B 通过促进 FAK 磷酸化信号通路促进肿瘤侵袭和增殖,并与非小细胞肺癌患者的不良临床结果相关
Authors Zhou X, Yang F, Zhang Q, Miao Y, Hu X, Li A, Hou G, Wang Q, Kang J
Received 7 January 2018
Accepted for publication 26 August 2018
Published 25 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7493—7501
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S161852
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Family with sequence similarity 129, member B (FAM129B ), also called MINERVA, is upregulated and promotes tumor invasion in multiple types of cancer. However, the mechanism and clinicopathological significance of FAM129B remains unclear.
Materials and methods: Online KM-plotter tool and immunohistochemistry were used to predict the prognostic value of FAM129B expression in lung cancer tissues. Western blotting analysis, MTT, colony formation assay and matrigel invasion assay were performed after overexpressing or depleting FAM129B .
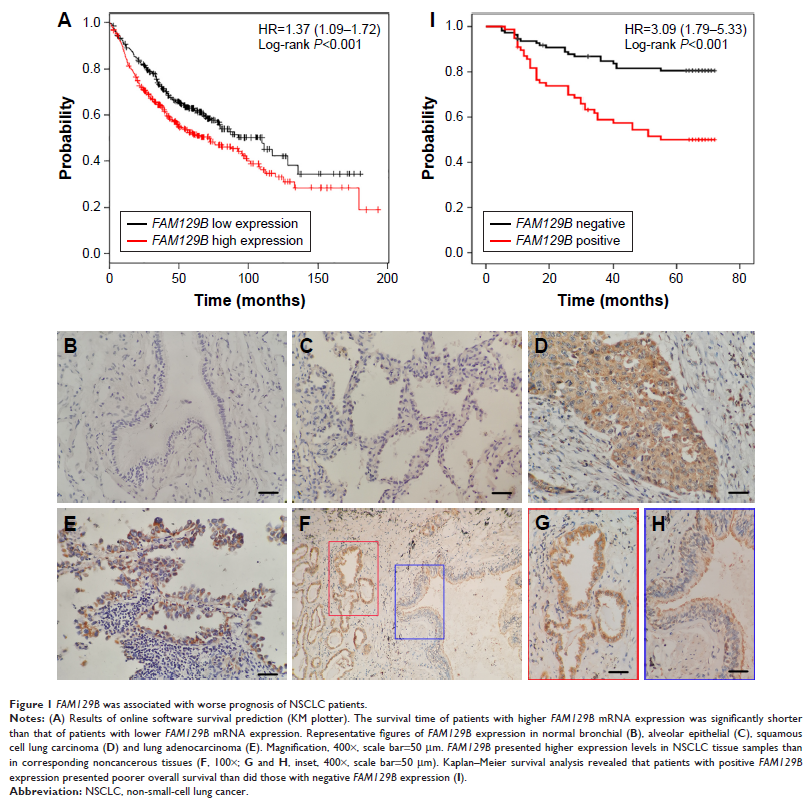
Results: In this study, using the online KM-plotter tool, we found FAM129B was correlated with adverse outcome in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (P <0.001). Immunohistochemistry results revealed that FAM129B showed negative or dim expression in normal lung tissues while presented positive cytoplasmic expression in both squamous cell lung carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. The positive ratio of FAM129B in clinical NSCLC tissue samples (77/187, 41.2%) was significantly higher than that in normal lung tissue samples (8/68, 11.8%; P <0.001). FAM129B expression associated with advanced TNM staging (P <0.001) and positive regional lymph node metastasis (P <0.001). The results of Kaplan-Meier analysis suggested that the survival time of patients with positive FAM129B expression was significantly shorter than those with negatively FAM129B expression (P <0.001). Proliferation and invasion assay revealed that FAM129B prominently facilitated tumor proliferation and invasion in NSCLC cells. Western blotting results revealed that FAM129B upregulated the expression of MMP2 and Cyclin D1 by enhancing the phosphorylation of FAK at Tyr 397 and Tyr 925. Incorporation of FAK inhibitor in the medium significantly downregulated the phosphorylation of FAK and subsequently attenuated increasing expression of MMP2 and Cyclin D1 induced by FAM129B overexpression.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that FAM129B may be a new prognosis predictor of NSCLC patients and impact tumor invasion and proliferation of NSCLC cells through promoting the activation of FAK signaling.
Keywords: FAM129B , invasion, proliferation, FAK, non-small cell lung cancer