110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

XRCC1 基因多态性与中国汉族人群骨肉瘤风险、临床病理特征及预后的关系
Authors Wu YG, Li HF, Ren YJ, Zou DB, Zhang KN, Xiao X
Received 16 June 2018
Accepted for publication 9 August 2018
Published 25 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4959—4967
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S177452
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Introduction: The association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms at X-ray repair cross-complementing group-1 (XRCC1) with osteosarcoma (OS) development has not been fully clear to date. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the association of XRCC1 polymorphisms with risk, clinicopathologic features, and prognosis in Chinese OS patients.
Methods: A total of 146 patients with primary OS and 248 age- and gender-matched controls were included in the present study. The frequencies of four XRCC1 polymorphisms (rs25487, rs1799782, rs25489, and rs3213245) were determined between OS patients and controls. The association of XRCC1 polymorphism with clinicopathologic characteristics, prognosis, and XRCC1 expression was further evaluated.
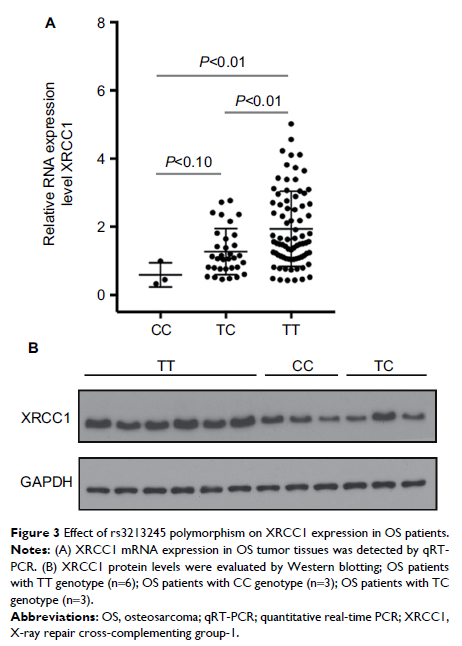
Results: Compared with TT genotype, individuals carrying the minor C allele (TC+ CC) of rs3213245 had significantly increased risk of OS development (OR =1.83, 95% CI 1.14–3.00). OS patients carrying TC genotype and C allele at rs3213245 were more likely to be with larger tumor size and metastasis. Survival analysis demonstrated that OS patients carrying C allele (TC + CC) at rs3213245 had shorter survival time than those with TT genotype. The T to C substitution at rs3213245 could decrease XRCC1 gene transcriptional activity in vitro. XRCC1 mRNA and protein expression levels were lower in OS patients carrying TC or CC genotype at rs3213245. Besides, no significant association of rs25487, rs1799782, and rs25489 with OS was observed.
Conclusion: In conclusion, these findings revealed that XRCC1 rs3213245 polymorphism was associated with increased risk of OS, which could affect XRCC1 expression in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: osteosarcoma, XRCC1, polymorphism, prognosis