108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

壳聚糖微胶囊化胰岛素通过调节糖尿病大鼠 COX-2 和 VCAM-1 的表达减轻肠系膜微循环功能障碍
Authors Xu J, Cao L, Suo Y, Xu X, Sun H, Xu S, Zhu X, Yu H, Cao W
Received 13 May 2018
Accepted for publication 2 October 2018
Published 25 October 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 6829—6837
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S174030
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
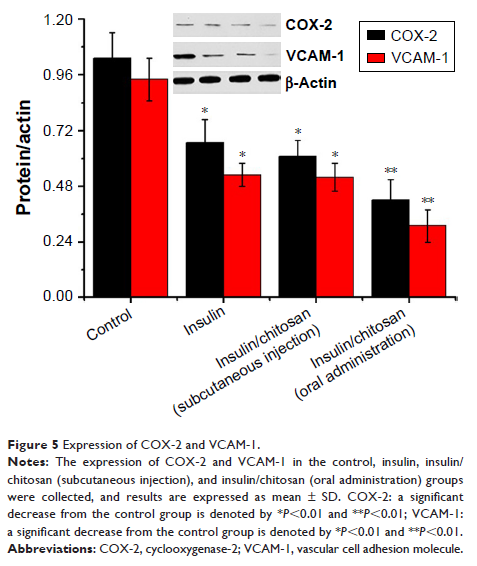
Background: The study of the experiment was to display the therapeutic function of insulin-loaded chitosan (insulin/chitosan) on mesenteric microcirculation via down-regulating cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) expressions in rats with diabetes mellitus (DM) as compared to free insulin.
Methods: Diabetic rats were administrated with 24 U/kg insulin or 120 U/kg insulin/chitosan compounds. The blood and mesenteriums were collected, blood glucose levels, arteriole velocity, arteriole diameter, venular diameter, and hemodiapedesis were measured, and COX-2, VCAM-1 expressions were measured in mesenteriums tissues.
Results: Both insulin and insulin/chitosan administration decreased blood glucose and improved the state of mesenteric microcirculation through down-regulating COX-2 and VCAM-1 expressions as compared to DM groups, while insulin/chitosan remarkably augmented this functions.
Conclusion: Chitosan-microcapsulated insulin alleviates mesenteric microcirculation dysfunction via modulating COX-2 and VCAM-1 expressions in rats with DM.
Keywords: insulin, chitosan, COX-2, VCAM-1