110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血浆纤维蛋白原在肝细胞癌中的预后价值:一项荟萃分析
Authors Huang G, Jiang H, Lin Y, Wu Y, Cai W, Shi B, Luo Y, Jian Z, Zhou X
Received 30 May 2018
Accepted for publication 26 July 2018
Published 29 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 5027—5041
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S175780
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Elevated plasma fibrinogen levels have been associated with tumor progression in several malignancies. Our study aims to characterize the clinical significance of elevated plasma fibrinogen levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and methods: Relevant published articles were systematically searched in electronic databases including PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science. The pooled differences in plasma fibrinogen levels among HCC, cirrhotic, and control groups were expressed as weighted mean differences (WMDs) and their corresponding 95% CIs. The associations between elevated fibrinogen and overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS)/recurrence-free survival (RFS) were expressed as HRs and their 95% CIs, whereas the associations between elevated fibrinogen and various types of clinical characteristic of patients with HCC were expressed as ORs and their corresponding 95% CIs.
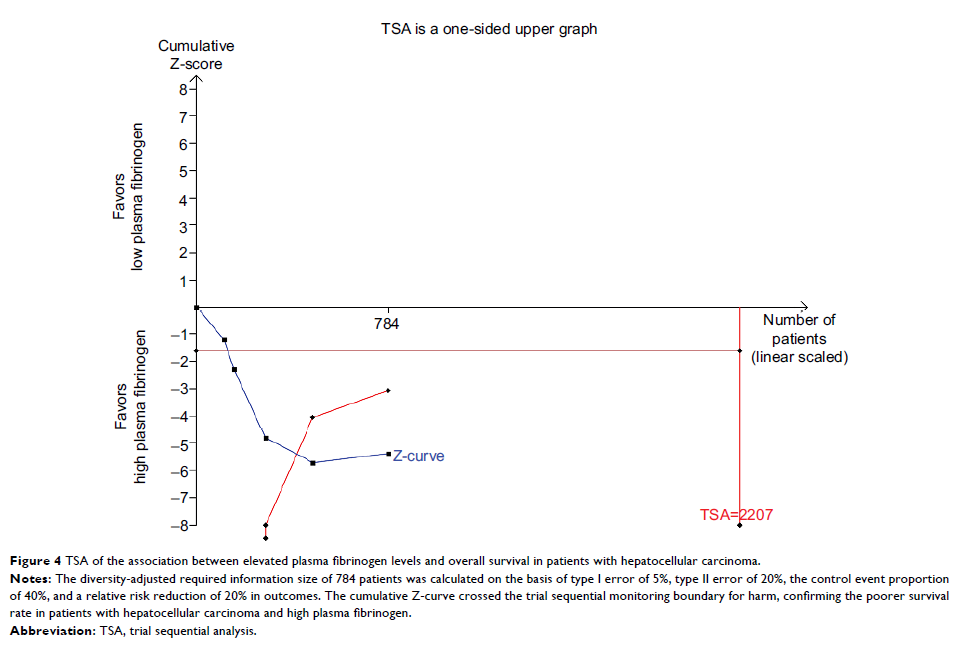
Results: Results showed that the plasma fibrinogen levels in patients with HCC were not significantly different than that in healthy controls (WMD = 0.50, 95% CI = [–0.82, 1.82], P = 0.457) or patients with cirrhosis (WMD = −0.62, 95% CI = [–1.56, 0.33], P = 0.200). However, our results showed that compared to those with normal levels, patients with HCC and elevated plasma fibrinogen levels showed poorer OS (HR = 2.08, 95% CI = [1.67, 2.59], P < 0.0001) and DFS/RFS (HR = 1.90, 95% CI = [1.52, 2.37], P < 0.0001). Results of trial sequential analysis of the OS indicated that currently available studies were sufficient to validate the negative prognostic value of elevated plasma fibrinogen in patients with HCC. Clinicopathological analyses showed that high plasma fibrinogen levels were associated with tumor progression as indicated by advanced tumor stage, larger tumor size, increased tumor number, and the presence of vascular invasion.
Conclusion: Elevated plasma fibrinogen levels are associated with poor prognosis and advanced tumor progression. Plasma fibrinogen may serve as a negative prognostic biomarker in patients with HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, fibrinogen, prognosis, tumor progression, meta-analysis