110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

源自 rAAV/AFP 转染的树突细胞外来体可引发特异性 T 细胞介导下的、针对肝细胞癌的免疫应答
Authors Li J, Huang SL, Zhou Z, Lin W, Chen S, Chen M, Ye Y
Received 26 June 2018
Accepted for publication 17 August 2018
Published 29 October 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 4945—4957
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S178326
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Dendritic cell (DC)-derived exosomes (Dexs) have been proved to induce and enhance antigen-specific T cell responses in vivo, and previous clinical trials have shown the feasibility and safety of Dexs in multiple human cancers. However, there is little knowledge on the efficacy of Dexs against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) until now.
Methods: In this study, human peripheral blood-derived DCs were loaded with recombinant adeno-associated viral vector (rAAV)-carrying alpha-fetoprotein (AFP ) gene (rAAV/AFP), and high-purity Dexs were generated. Then naive T cells were stimulated with Dexs to investigate the specific T cell-mediated immune responses against HCC.
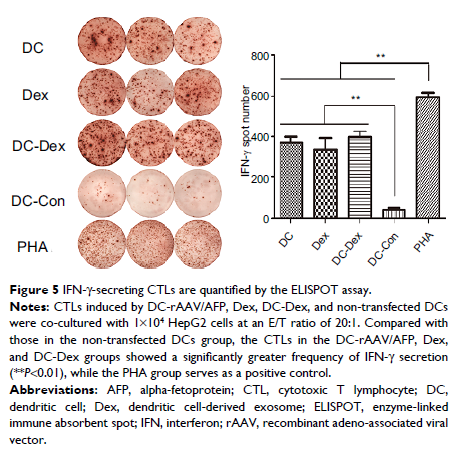
Results: Our findings showed that Dexs were effective to stimulate naive T cell proliferation and induce T cell activation to become antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), thereby exhibiting antitumor immune responses against HCC. In addition, Dex-sensitized DC precursors seemed more effective to trigger major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I)-restricted CTL response and allow DCs to make full use of the minor antigen peptides, thereby maximally activating specific immune responses against HCC.
Conclusion: It is concluded that Dexs, which combine the advantages of DCs and cell-free vectors, are promising to completely, or at least in part, replace mature DCs (mDCs) to function as cancer vaccines or natural antitumor adjuvant.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, dendritic cell, exosome, immune response, cytotoxic T lymphocyte