110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

具有二硫键的肽 T7 修饰的多肽用于靶向递送用于前列腺癌基因治疗的质粒 DNA
Authors Lu Y, Jiang W, Wu X, Huang S, Huang Z, Shi Y, Dai Q, Chen J, Ren F, Gao S
Received 20 July 2018
Accepted for publication 19 September 2018
Published 30 October 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 6913—6927
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S180957
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
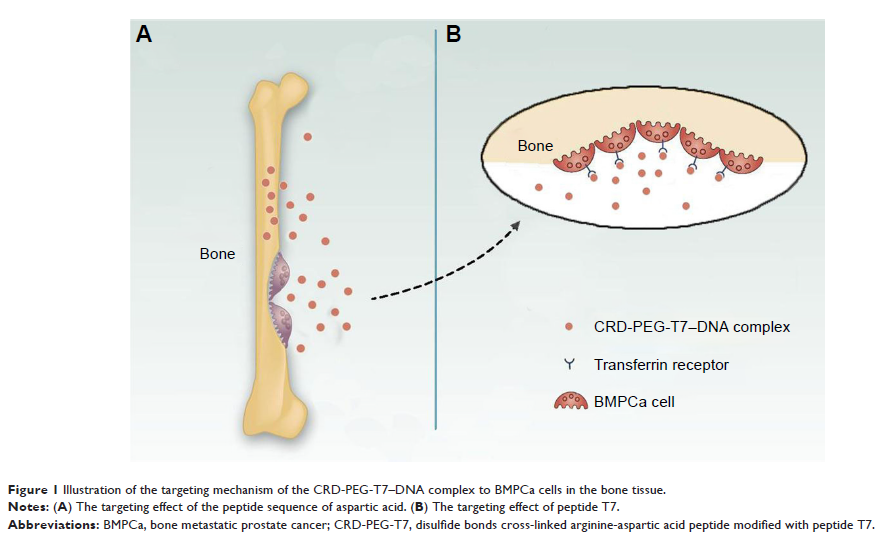
Methods: The structure of CRD-PEG-T7 was determined and the cellular uptake efficacy, gene transfection efficacy, cytotoxicity, and the targeting effect of the CRD-PEG-T7–plasmid DNA complex were examined.
Results: The results demonstrated that the CRD-PEG-T7–plasmid DNA complex was nanosized and had a positively charged surface, good cellular uptake efficacy, minimal cytotoxicity, and a dual-targeting effect as compared with the CRD-PEG–plasmid DNA complex. The peptide T7-modifed new delivery system was able to target the highly expressed transferrin receptor (TfR) on tumor cells with an efficiency four-fold higher than that of the non-modified system.
Conclusion: The results above indicatd that the CRD-PEG-T7–plasmid DNA complex may prove to be a promising gene delivery system targeting bone-metastatic tumor.
Keywords: arginine peptide, aspartic acid peptide, tumor targeting, DNA delivery, bone metastasis prostate cancer