110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

阿法替尼通过抑制 NRG1 通路逆转 ALK/ROS1 阳性非小细胞肺癌细胞(NSCLC)中的 ceritinib 耐药性(CR)
Authors Chen H, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Jia B, Zhang B, Wang C
Received 3 May 2018
Accepted for publication 25 June 2018
Published 26 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8201—8209
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S173008
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Lung
cancer (LC) is the most prevalent malignancy worldwide, and non-small-cell LC
(NSCLC) cell is associated with high mortality. As a member of the second
generation of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) suppressors, ceritinib has
considerable therapeutic effects for ALK and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1)-positive
NSCLC cell. Nevertheless, patients inevitably develop resistance to the drug.
Our research focused on the exploration of whether afatinib was able to
counteract ceritinib resistance (CR) in NSCLC cells with positive ALK or ROS1.
Materials and methods: Acquired
CR cell sublines (HCC78R and H1299R) were induced by stepwise escalation of
ceritinib exposure. MTT assay was used to validate cell proliferation.
Fluorescence assay was performed for apoptosis analysis. Quantitative real-time
PCR and Western blot assays were used to assess the alterations of signaling
pathway-related mRNA and proteins, respectively.
Results: We found
that prolonged treatment of HCC78 and H1299 with ceritinib brought about 10
times weaker ceritinib sensitivity (CS) in comparison with parent cells.
Additionally, the results showed that afatinib efficiently promoted CS, which
was evidenced as reduced proliferation and cell death promotion, in NSCLC
cells, irrespective of their previous sensitivity or resistance to ceritinib.
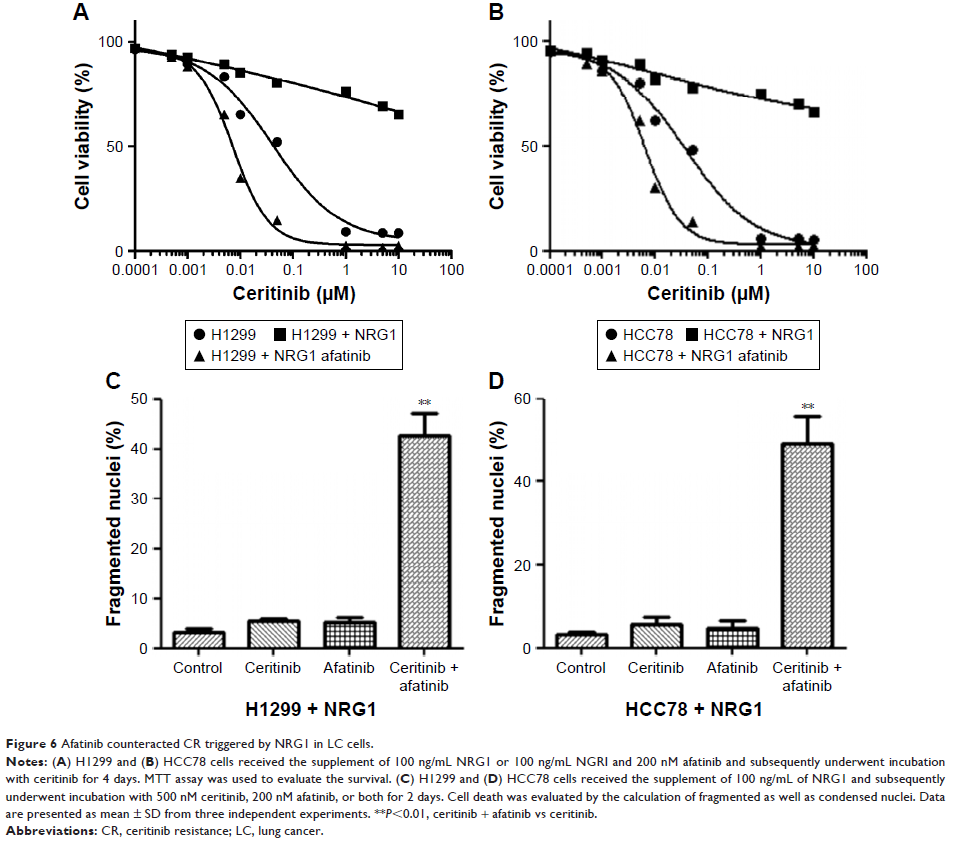
Moreover, afatinib decreased neuregulin-1 (NRG1) signaling stimulation in CR as
well as CS cells. Furthermore, supplementing NRG1 in H1299 and HCC78 cells
triggered CR, which was attenuated by afatinib.
Conclusion: These
results demonstrated that afatinib overcame CR in NSCLC cells with positive ALK
or ROS1 by inhibiting the NRG1 signaling pathway, which might be a promising
therapeutic approach.
Keywords: afatinib,
ceritinib, NRG1, lung cancer, ALK/ROS1