110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利多卡因逆转糖尿病库普弗细胞(Kupffer cell)功能失调的吞噬能力、粒细胞募集和炎症因子的分泌
Authors Wang R, Sheng M, Shi F, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Wu J, Wu G, Song Q
Received 6 September 2018
Accepted for publication 17 October 2018
Published 26 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 827—834
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S186695
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Juei-Tang Cheng
Purpose: Kupffer
cells (KCs) present dysfunctional immunity capacity among the diabetes mellitus
patients. This study aims to investigate whether Lidocaine could reverse
dysfunctions of KCs, in terms of phagocytosis, granulocyte recruitment and
inflammatory mediator secretion.
Methods: db/db and
C57BL/6 mice were employed to establish diabetic and nondiabetic models. Upon
intravenous injection of Lidocaine, KCs were isolated and cultured ex vivo. The
functions of phagocytosis, recruiting granulocytes and inflammatory mediator
secretion in KCs were compared between Lidocaine-treated and untreated
(control) groups.
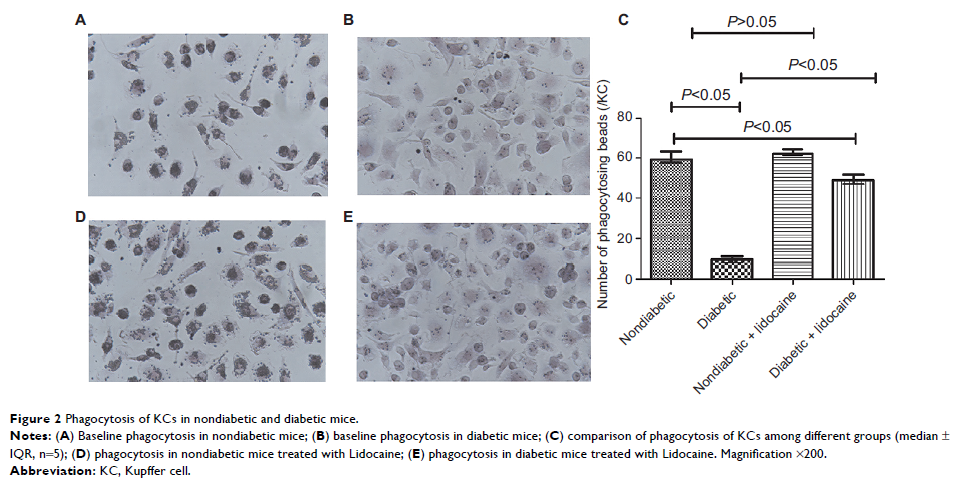
Results: Comparing
with nondiabetic mice, KCs in diabetic mice presented reduced phagocytosis,
activated granulocyte recruitment, increased expression of intercellular cell
adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and activated levels of inflammatory mediators.
With Lidocaine injection, phagocytic functions of KCs in diabetic mice were
improved significantly; in contrast, recruitment of granulocytes, expression of
ICAM-1 and secretion of inflammatory mediators were reduced markedly. However,
Lidocaine intervention did not alter KC functions in phagocytosis, granulocyte
recruitment, ICAM-1 expression or inflammatory mediator secretion among
nondiabetic mice.
Conclusion: Lidocaine
reversed diabetes-related dysfunctions of KCs in terms of phagocytosis,
granulocyte recruitment, ICAM-1 expression or inflammatory mediator secretion.
Keywords: macrophages,
diabetes, phagocytosis, granulocyte recruitment, inflammatory mediator,
Lidocaine