110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Let-7a 通过靶向 Aurora-B 抑制骨肉瘤细胞生长和肺转移
Authors Yu JJ, Pi WS, Cao Y, Peng AF, Cao ZY, Liu JM, Huang SH, Liu ZL, Zhang W
Received 23 August 2018
Accepted for publication 16 October 2018
Published 26 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6305—6315
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S185090
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Purpose: Accumulating
studies showed that the expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) was dysregulated in
osteosarcoma (OS). In this study, we sought to investigate the effect of let-7a
on OS progression and its potential molecular mechanism.
Patients and methods: Quantitative
real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to evaluate the expression level of
let-7a and Aurora-B (AURKB) in OS tissues and cells. The OS cells were treated
with let-7a mimic, let7a inhibitor, negative mimic and Lv-AURKB combined with
let-7a. The ability of cell proliferation, migration and invasion was measured
using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and wound-healing and transwell invasion
assays. The protein of AURKB, NF-κβp65, MMP2 and MMP9 was measured by Western
blot analysis. Xenograft model was performed to investigate the effects of
let-7a on tumor growth and metastasis. The lung metastasis was measured by
counting the metastatic node using H&E staining.
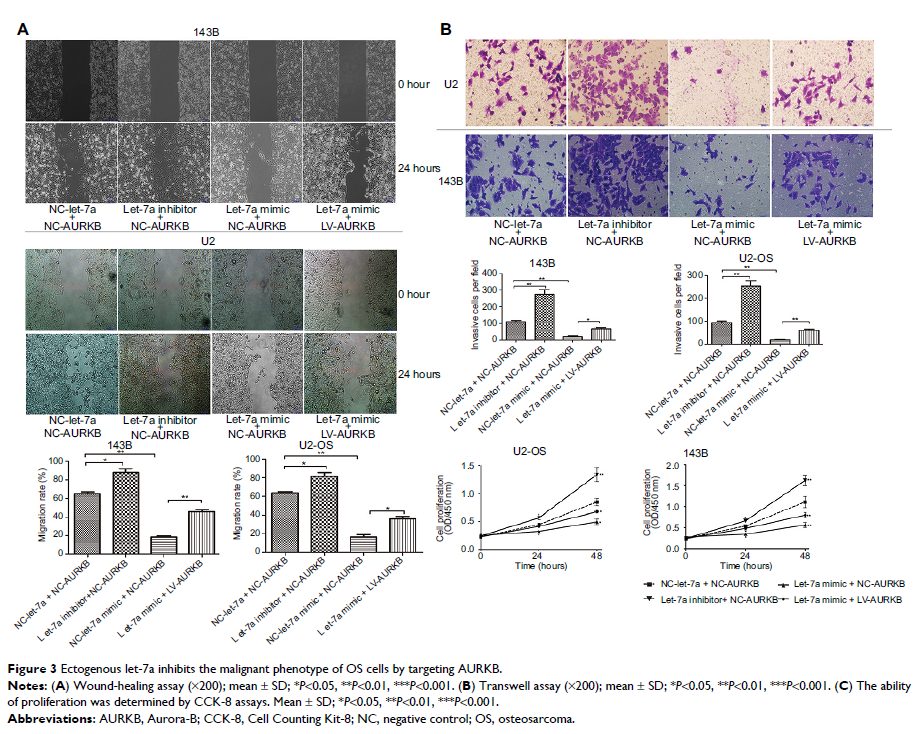
Results: Let-7a
expression was significantly underexpressed in OS cell lines and tissues
compared with human osteoblast cell lines, hFOB1.19, and adjacent normal bone
tissues. Exogenous let-7a inhibited the viability, migratory and invasive
ability of OS cells in vitro. In addition, the overexpression of AURKB in OS
cells could partly rescue let-7a-mediated tumor inhibition. Also, the
overexpression of let-7a inhibited OS cell growth and lung metastasis in vivo.
Furthermore, the results showed that let-7a could decrease the expression of
NF-κβp65, MMP2 and MMP9 proteins by targeting AURKB in OS cells.
Conclusion: Let-7a
inhibits the malignant phenotype of OS cells by targeting AURKB at least
partially. Targeting let-7a and AURKB/NF-κβ may be a novel therapeutic strategy
for the treatment of OS.
Keywords: let-7a,
Aurora-B, osteosarcoma, malignant phenotype