110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

吡咯啉-5-羧酸还原酶1通过抑制人恶性黑素瘤中的细胞凋亡来促进细胞增殖
Authors Ye Y, Wu Y, Wang J
Received 27 February 2018
Accepted for publication 2 July 2018
Published 27 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6399—6407
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S166711
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Introduction: Human malignant
melanoma (MM) is a highly malignant tumor of cutaneous melanocytes with a fast
progression. We investigated the cellular effects of pyrroline-5-carboxylate
reductase 1 (PYCR1) in the MM cell lines, A375 and M14.
Methods: Cell
Counting Kit-8 assay, transwell assay, and flow cytometry analysis were
performed to evaluate the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of MM cell
lines, respectively. To gain more insight into the role of PYCR1 in tumor
growth, we analyzed the AKT phosphorylation level in PYCR1-specific siRNA
(siPYCR1) and negative control (NC) cells.
Results: Biochemical
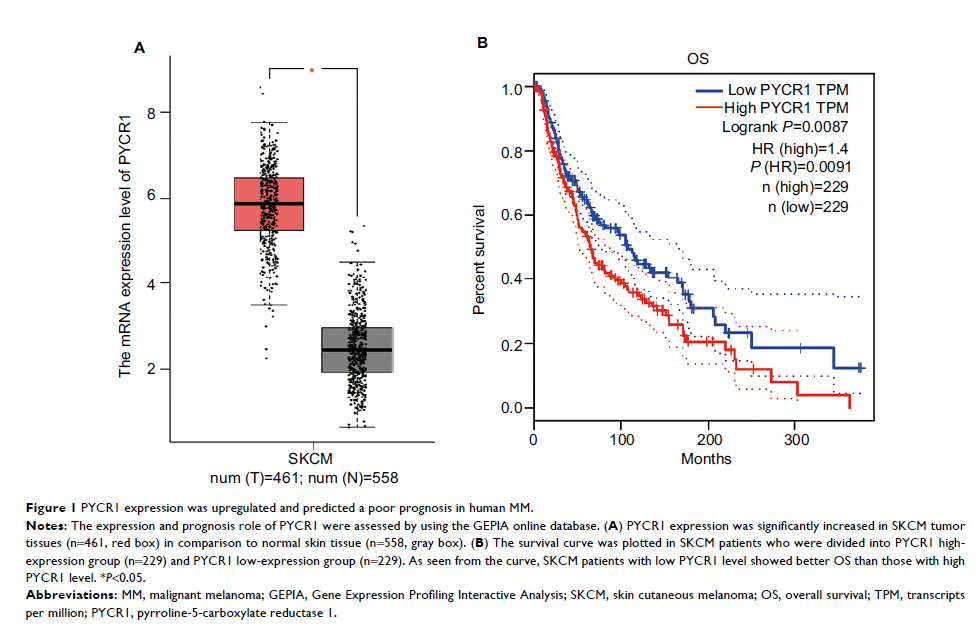
analysis revealed a clear increase in PYCR1 expression in human MM samples, and
its high expression predicted a poor prognosis. Silencing of PYCR1 suppressed
the proliferation and migration of A375 and M14 cells. The percentage of apoptosis
in cells transfected with siPYCR1 significantly increased in comparison to that
of cells transfected with negative control siRNA (NC). The enhanced apoptosis
in PYCR1 knockdown cells was consistent with an increased level of markers of
apoptosis. siPYCR1 inhibited AKT phosphorylation, as well as the expression of
its downstream protein, P70, suggesting that PYCR1 promoted cell growth of the
MM cell lines A375 and M14 through stimulation of the AKT pathway. Moreover,
forkhead box K2 and regulatory associated protein of MTOR complex 1 shared a
similar expression pattern to that of PYCR1 and were significantly
downregulated in PYCR1 knockdown cells.
Conclusion: PYCR1
promoted tumor progression through the AKT pathway in human MM in vitro. Our
results expand the knowledge of PYCR1 functions in solid tumors and provide a
potential target for the clinical treatment of human MM.
Keywords: apoptosis;
proliferation; prognosis; AKT pathway