110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

XRCC1 rs1799782 (C194T) 多态性与乳腺癌的肿瘤转移和分子亚型相关
Authors Li Q, Ma R, Zhang M
Received 21 October 2017
Accepted for publication 26 August 2018
Published 28 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8435—8444
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S154746
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Breast cancer,
a malignant tumor with its highest incidence in women, affects physical and
mental health, and can even be life-threatening. In recent years, its incidence
has continued to grow, accompanied by a trend of younger onset. XRCC1 is well
known as a DNA-repair gene, and its abnormal expression is related to the
occurrence of various malignant tumors.
Methods: In this study,
we detected XRCC1 expression and investigated its association
with the XRCC1 rs1799782
polymorphism. XRCC1 was overexpressed to investigate its effect
on in breast cancer cells. CCK8 and clone formation efficiency assay were used
to detect cell proliferation. Transwell assay was performed to confirm cell
migration and invasion. Flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis.
Results: In 118 breast
cancer samples, CC genotype frequency was 49.15% (58 of 118), CT genotype
frequency was 42.37% (50 of 118), and TT genotype frequency was 8.48% (ten of
118). Lymphatic metastasis was associated with a higher frequency of XRCC1 rs1799782
polymorphism (P <0.05),
and breast cancer patients with positive PR, HER2, and negative ER had
high XRCC1 rs1799782
frequency (P <0.05).
Meanwhile, XRCC1 had
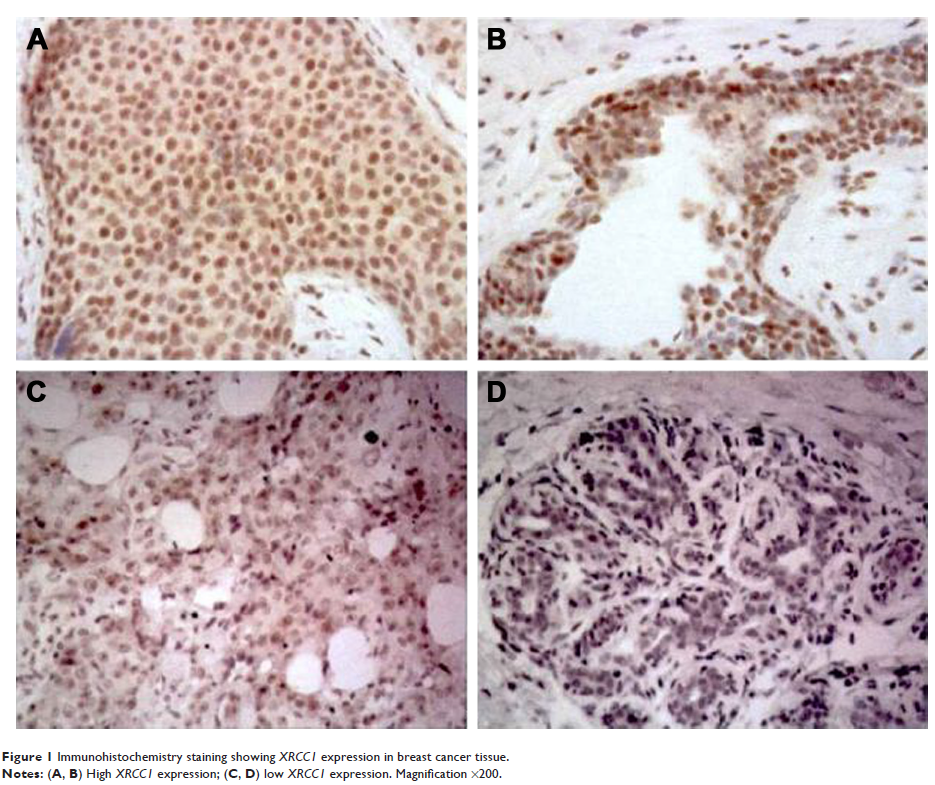
low expression in breast cancer (74.6%, 88 of 118) and high expression in
ER-negative, PR-negative, HER2-positive and Ki67-low-expression patients. XRCC1 rs1799782
may play an important role in the development and metastasis of breast cancer.
These results differ from previous studies that did not suggest that rs1799782
is effective in breast cancer. We also investigated the role of XRCC1 in
breast cancer progression.
Conclusion: We have proved
that XRCC1 can
inhibit proliferation and invasion and promote apoptosis of breast cancer
cells. XRCC1 expression
was regulated by the JNK pathway. We found that the JNK inhibitor SP600125
significantly inhibited the growth of breast cancer cells, and consider it a
potential drug for breast cancer.
Keywords: MCF7,
gene expression, proliferation, apoptosis, JNK pathway