110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

立体定向放射治疗早期非小细胞肺癌完全切除患者的新发肺部肿瘤的临床疗效
Authors Zhao Q, Chen G, Ye L, Zeng Z, Shi S, He J
Received 16 July 2018
Accepted for publication 19 October 2018
Published 28 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6391—6398
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S180345
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Purpose: Following
surgery for early stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), de novo pulmonary
tumors are common. This study aimed to assess the efficacy, patterns of
failure, and toxicity of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in the treatment
of de novo pulmonary tumors following curative resection of early stage NSCLC.
Patients and methods: We
reviewed the medical data of patients who had received definitive intent SBRT
for small lung cancer at Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, between June
2011 and December 2017. Patients who had experienced complete resection for
prior early stage NSCLC before SBRT were identified for further analysis.
Incidences of locoregional recurrence (LR) and distant metastasis (DM) were
evaluated using the alternative cumulative incidence competing risk method. The
probability of survival was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method.
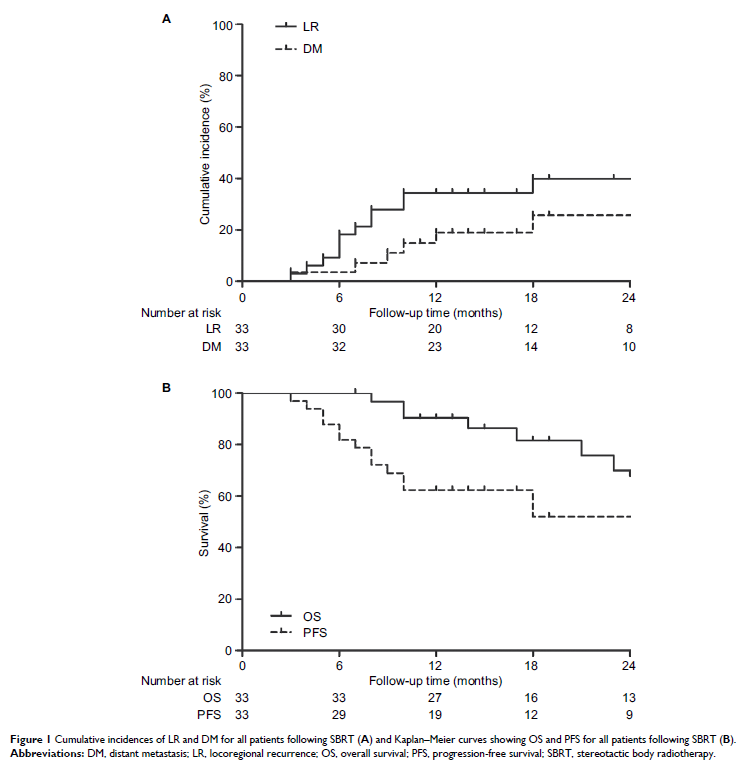
Results: A total of 33
patients with 36 lesions were eligible and included in this study. The median
follow-up time was 32 months. Estimated incidences of LR and DM were 37.62% and
15.92%, respectively, at 1 year and 48.02% and 21.23%, respectively, at 2
years. The progression-free survival and overall survival of all patients were
62.40% and 90.30%, respectively, at 1 year and 52.00% and 69.90%, respectively,
at 2 years. In all, 26 patients experienced grade 1 SBRT-related toxicity, 11
patients experienced grade 2 SBRT-related toxicity, and three patients
experienced grade 3 toxicity. There were no grade 4/5 toxicities or
SBRT-related deaths during the follow-up period.
Conclusion: SBRT appears to
be a safe and potentially effective alternative therapeutic option for de novo
pulmonary tumors following early stage NSCLC radical resection, despite
impaired pulmonary reserve.
Keywords: stereotactic
body radiotherapy, de novo pulmonary tumors, surgical resection, clinical
outcomes