110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 EZH2 和 EGFR 的抑制可通过增加胃癌细胞中的自噬而对细胞凋亡产生协同效应
Authors Yang Y, Zhu F, Wang Q, Ding Y, Ying R, Zeng L
Received 5 September 2018
Accepted for publication 17 October 2018
Published 29 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8455—8463
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S186498
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background: Numerous
reports have shown that a combination of two or more drugs leads to better
cancer treatment. Inhibitors of zeste homology 2 and epidermal growth factor
receptor have been widely used in cancer treatments. However, the mechanisms of
the combined use of these two drugs remain elusive.
Methods: Sulforhodamine
B assays and Alexa Fluor®-488 Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit were
used to detect the cell proliferation and cell apoptosis in vitro,
respectively. Western blotting analysis was used to detect the relative protein
expression, and xenografted tumor was generated in nude mice to evaluate the
effect in vivo.
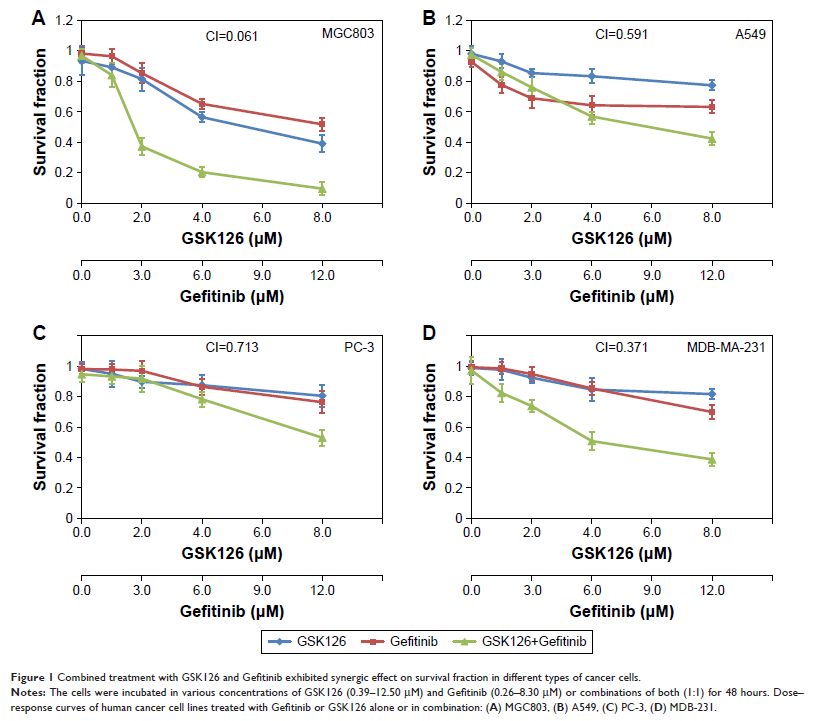
Results: Treatment with
either Gefitinib ranging from 0 to 12.5 µM or GSK126 ranging from 0 to 8.3 µM
caused a dose-dependent decrease in the cell survival fraction, and the
combination of Gefitinib at 12.5 µM and GSK126 at 8.3 µM caused further
significant decrease. The combination indexes were 0.061, 0.591, 0.713, and
0.371 for MGC803, A549, PC-3, and MDB-MA-231, respectively. In MGC803 cells,
the combination of GSK126 and Gefitinib synergistically induced cell apoptosis
(56.2%), which was markedly higher as compared to either drug alone (7.6% and
10.6%, P <0.05).
Treatment with either Gefitinib or GSK126 alone induced a significant increase
in cell apoptosis in LC3-II and p-ULK, whereas the combination of the two
induced a further increase. Pretreatment with an autophagy inhibitor,
3-methyladenine, prevented the apoptosis induced by the combined use of
Gefitinib and GSK126. In addition, the combined use of Gefitinib and GSK126
also inhibited the activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling
pathway. Furthermore, the combined use of GSK126 and Gefitinib synergistically
inhibited xenografted tumor proliferation.
Conclusion: The combined
use of GSK126 and Gefitinib exerts a synergic effect on tumor growth inhibition
both in vitro and in vivo through inducing autophagy and promoting apoptosis.
Therefore, GSK126 and Gefitinib in combination may be considered as a potential
strategy in treating solid tumor clinically.
Keywords: EZH2, EGFR,
autophagy, mTOR signaling, gastric cancer