110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

与 p38MAPK 相关的 uPA 在食管癌中的高表达表明预后不良
Authors Liu Q, Li W, Yang S, Liu Z
Received 28 July 2018
Accepted for publication 5 October 2018
Published 29 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8427—8434
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S181701
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: The aim of the
study was to investigate the relationship between urokinase-type plasminogen
activator (uPA) and mitogen-activated protein kinase 38 (p38MAPK), and preliminarily
analyze their relationship with clinical characteristics of esophageal
cancer.
Materials and methods: Immunohistochemistry
and Western blot were used to detect the expressions of uPA and p38MAPK in
patients with esophageal cancer. The relationship between them and
clinicopathological features was analyzed by chi-squared test and Spearman
correlation. Prognosis was performed using Kaplan–Meier and Cox proportional
hazard models analysis.
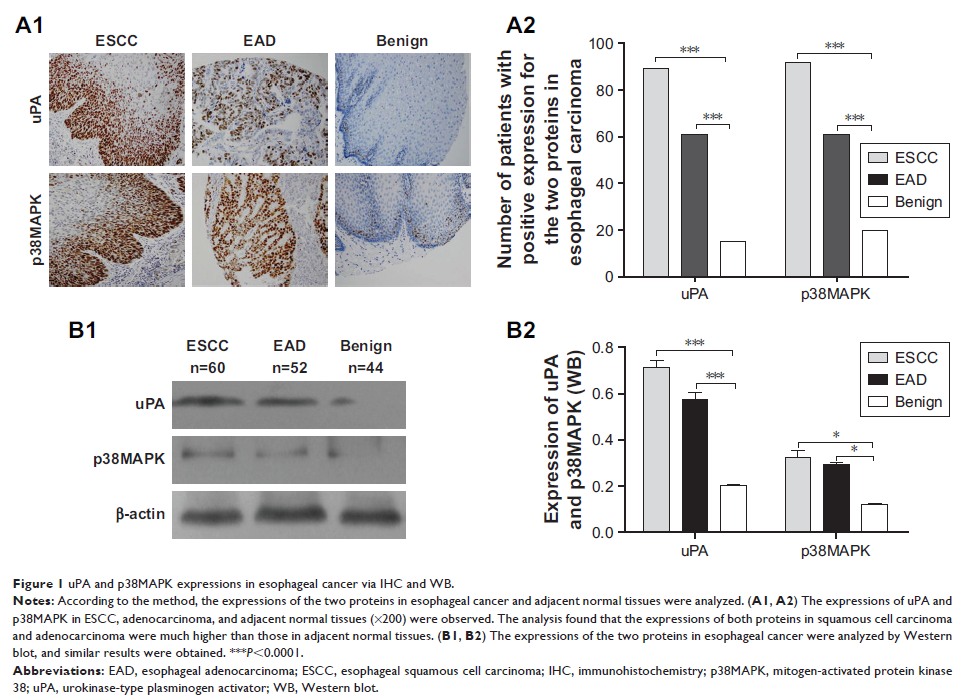
Results: The
expressions of uPA and p38MAPK proteins were significantly higher in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma than in normal esophageal mucosa
tissue (both P <0.0001). The expression of uPA was significantly
correlated with the depth of invasion of esophageal cancer (P =0.0067), tumor
size (P =0.0364),
and pathological stage (P <0.0001); p38MAPK expression vs esophageal cancer
tissue type (P =0.0043),
esophageal cancer infiltration depth (P =0.0097), tumor size (P =0.0015), and
pathological stage (P <0.0001). Both were not significantly associated
with lymph node staging, gender, age, and esophageal cancer histological type.
There was a positive correlation between uPA and p38MAPK expressions (r =0.7301, P =0.0104).
Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that the overall survival time of patients with
positive expression of uPA or p38MAPK protein was significantly shorter, and
the time of recurrence or metastasis of esophageal cancer was significantly
earlier in patients with uPA-positive expression. Multivariate analysis of Cox
model showed that uPA, p38MAPK, and pathological staging were independent
factors influencing survival.
Conclusion: The
expressions of uPA and p38MAPK may play an important role in the progression of
esophageal cancer, and there is a close relationship between the two proteins,
which may be one of the prognostic indicators.
Keywords: esophageal
cancer, urokinase-type plasminogen activator, mitogen-activated protein kinase
38, prognosis