110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

贝前列素钠预处理可通过 P38 和 JNK 通路预防小鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤时的炎症、细胞凋亡和自噬
Authors Deng J, Feng J, Liu T, Lu X, Wang W, Liu N, Lv Y, Liu Q, Guo C, Zhou Y
Received 2 August 2018
Accepted for publication 17 October 2018
Published 29 November 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4067—4082
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S182292
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Cristiana Tanase
Objective: The goal
of this study was to determine the effects of beraprost sodium (BPS)
preconditioning on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury and its underlying
mechanisms of action.
Materials and methods: Mice were
randomly divided into sham, IR, IR+BPS (50 µg/kg), and IR+BPS (100 µg/kg)
groups. Saline or BPS was given to the mice by daily gavage for 1 week before
the hepatic IR model was established. Liver tissues and orbital blood were
collected at 2, 8, and 24 hours after reperfusion for the determination of
liver enzymes, inflammatory mediators, apoptosis- and autophagy-related
proteins, key proteins in P38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) cascades, and
evaluation of liver histopathology.
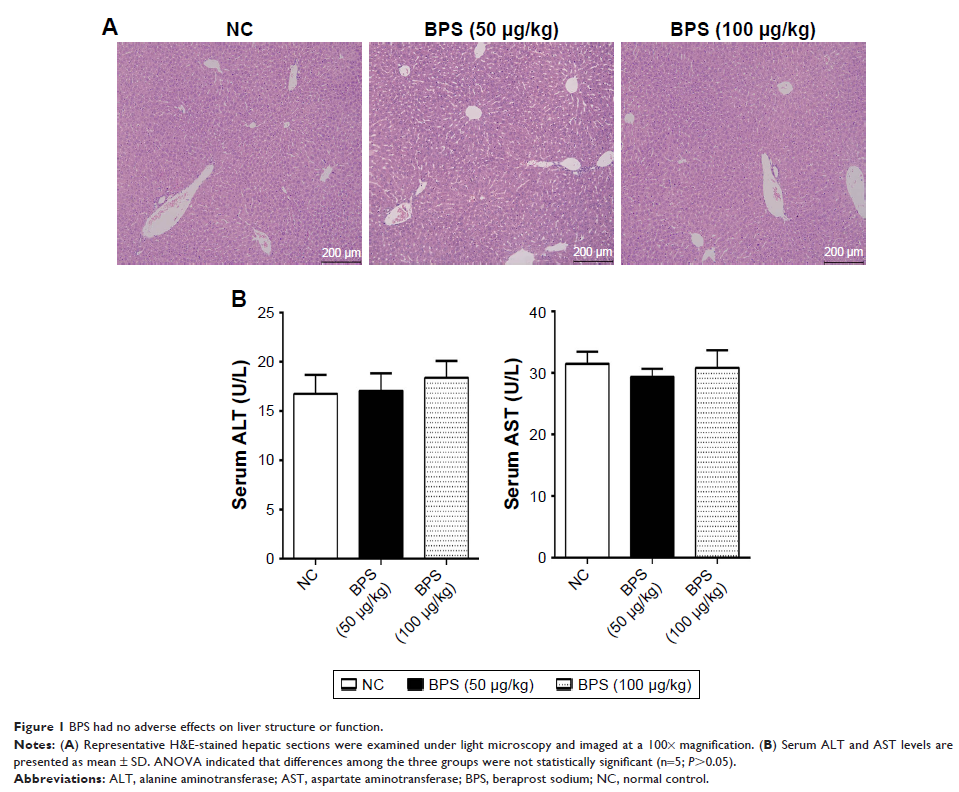
Results: BPS
preconditioning effectively reduced serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and
aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, improved pathological damage,
ameliorated production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β
(IL-1β), and affected expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, and
Caspase-9, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), Beclin-1, and
P62. The protective effects of BPS preconditioning were associated with reduced
P38 and JNK phosphorylation.
Conclusion: BPS
preconditioning ameliorated hepatic IR injury by suppressing inflammation,
apoptosis, and autophagy, partially via inhibiting activation of the P38 and
JNK cascades.
Keywords: liver
injury, beraprost sodium, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, MAPK pathway