110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

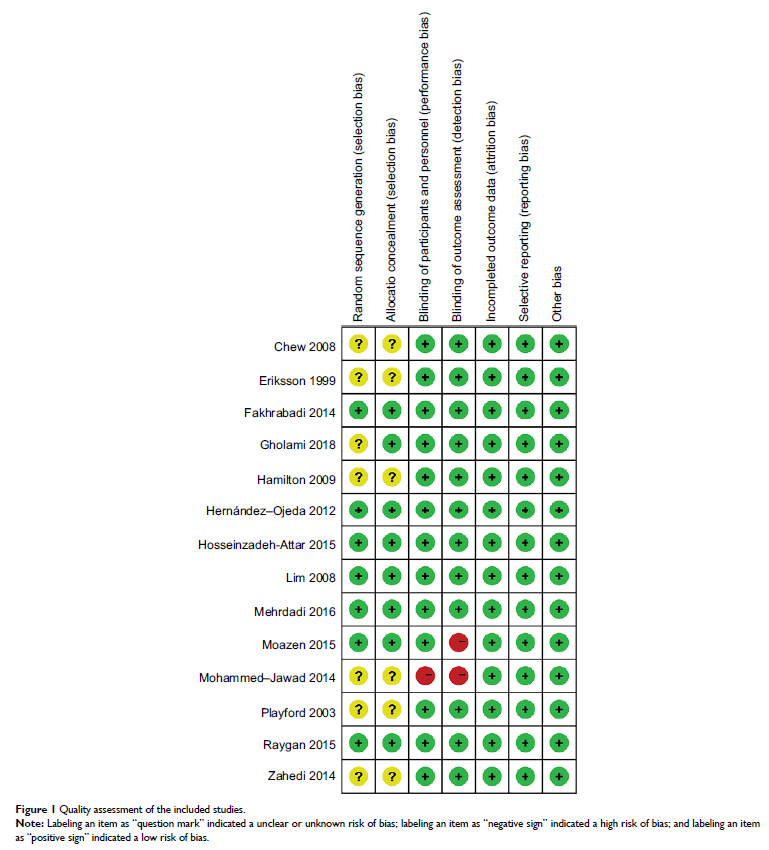
辅酶 Q10 对超重和肥胖 2 型糖尿病患者心血管和代谢生物标志物的影响: 一项汇总分析
Authors Huang H, Chi H, Liao D, Zou Y
Received 17 August 2018
Accepted for publication 5 October 2018
Published 29 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 875—886
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S184301
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Steven F. Abcouwer
Background: The potential
effects of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplementation in overweight/obese patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus are not fully established. In this article, we
aimed to perform a pooled analysis to investigate the effects of CoQ10 intervention
on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors in overweight/obese patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: MEDLINE,
Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched for randomized controlled trials
that evaluated the changes in CVD risk factors among overweight and obese patients
with T2DM following CoQ10 supplementation. Two investigators
independently assessed articles for inclusion, extracted data, and assessed
risk of bias. Major endpoints were synthesized as weighted mean differences
(WMDs) with 95% CIs. Subgroup analyses were performed to check the consistency
of effect sizes across groups. Publication bias and sensitivity analysis were
also performed.
Results: Fourteen
eligible trials with 693 overweight/obese diabetic subjects were included for
pooling. CoQ10 interventions significantly reduced
fasting blood glucose (FBG; –0.59 mmol/L; 95% CI, −1.05 to –0.12; P =0.01), hemoglobin
A1c (HbA1c; –0.28%; 95% CI−0.53 to –0.03; P =0.03), and
triglyceride (TG) levels (0.17 mmol/L; 95% CI, −0.32 to –0.03; P =0.02). Subgroup
analysis also showed that low-dose consumption of CoQ10 (<200
mg/d) effectively reduces the values of FBG, HbA1c, fasting blood insulin,
homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance, and TG. CoQ10 treatment was
well tolerated, and no drug-related adverse reactions were reported.
Conclusion: Our
findings provide substantial evidence that daily CoQ10 supplementation
has beneficial effects on glucose control and lipid management in overweight
and obese patients with T2DM.
Keywords: coenzyme
Q10, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular risk factors, lipids, glucose,
obesity