110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抑制 GIT1 可减少骨肉瘤的生长、侵袭和血管生成
Authors Zhang Z, Hu P, Xiong J, Wang S
Received 22 July 2018
Accepted for publication 21 October 2018
Published 29 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6445—6455
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S181066
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: GIT1, a
scaffold protein with ubiquitous multi-domain, is involved in many cellular
processes. In recent years, it was proved that GIT1 participated in various
tumors’ growth or metastasis. However, the biological function of GIT1 in
osteosarcoma is still unclear. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role and
mechanism of GIT1 in osteosarcoma.
Materials and methods: Human
osteosarcoma tissues were obtained to investigate the distribution of GIT1.
Adequate osteosarcoma cells were stably infected with lentivirus to knockdown
GIT1 level and then was used to carry out cell invasion and vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) assay in vitro. Orthotopic femoral
osteosarcoma model was constructed to investigate the growth, invasion, and
angiogenesis in vivo. Western blot was used to detect extracellular signal-regulated
kinase (ERK1/2) activation and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1α) expression.
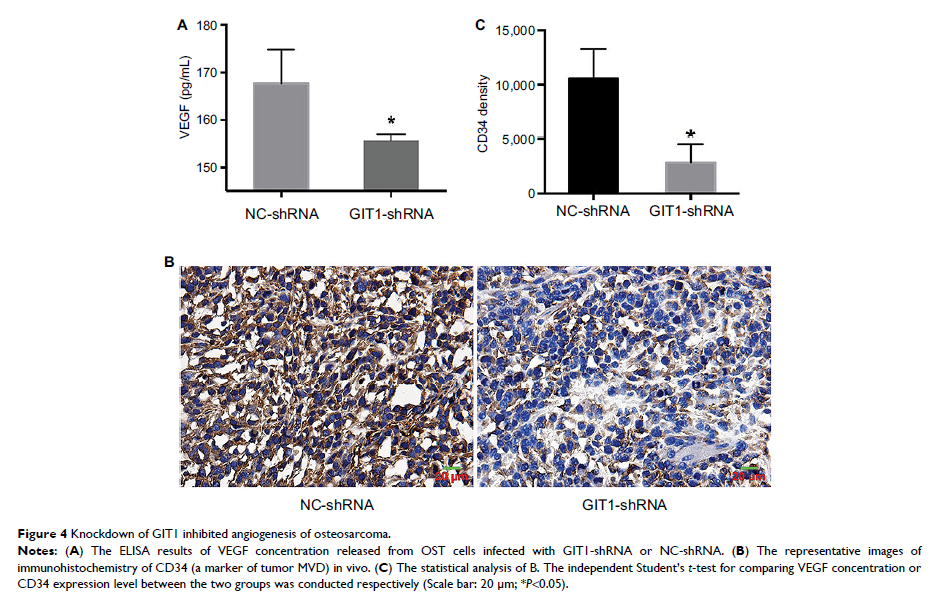
Results: In this
study, we found that GIT1 was distributed in human osteosarcoma tissues and
highly expressed in osteosarcoma (OS) cells. Knockdown of GIT1 inhibited cell
invasion and VEGF release in vitro and suppressed tumor growth, invasion, and
angiogenesis in vivo. Furthermore, knockdown of GIT1 substantially
downregulated the protein levels of p-ERK and HIF-1α in OST cells and
inhibition of p-ERK by PD98059 could significantly decrease the expression of
HIF-1α and concentration of VEGF in GIT1-shRNA-treated cells.
Conclusion: GIT1
knockdown can effectively inhibit the growth, invasion, and angiogenesis of
osteosarcoma. Thus, GIT1 might act as an oncogenic factor in osteosarcoma and
could be a potential molecular target for osteosarcoma gene therapy.
Keywords: GIT1,
osteosarcoma, angiogenesis, orthotopic femoral osteosarcoma model, ERK1/2,
HIF-1α