110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对于 EGFR 突变的晚期 NSCLC 患者进行 EGFR-TKIs 联合化疗、单独化疗或仅使用 EGFR-TKIs 的比较
Authors Wen M, Xia J, Sun Y, Wang X, Fu X, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Li X
Received 26 March 2018
Accepted for publication 11 September 2018
Published 30 November 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 183—190
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BTT.S169305
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Doris Benbrook
Purpose: Both
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and
chemotherapy are widely applied for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR mutations, and the combination of EGFR-TKIs and
chemotherapy has been used for advanced NSCLC patients; however, little is
known about the efficacy of the direct comparison among them.
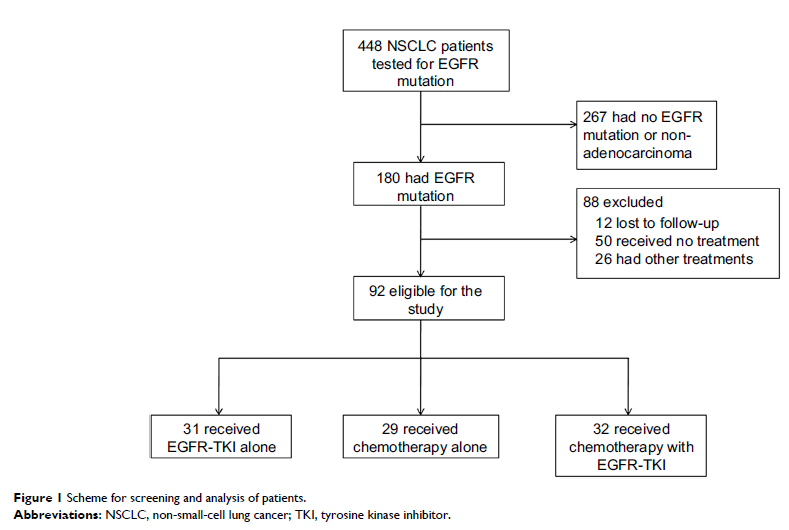
Patients and methods: The
demographic and clinical characteristics of 92 patients harboring advanced
NSCLC with EGFR mutation were retrospectively reviewed. We evaluated the
effects of EGFR-TKIs, chemotherapy, and EGFR-TKIs plus chemotherapy on advanced
NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations, and the efficacy of combination of
chemotherapy and EGFR-TKIs vs chemotherapy or EGFR-TKIs alone in advanced NSCLC
patients was evaluated.
Results: The
statistical results showed that the intercalated combination of EGFR-TKIs plus
chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS; HR, 1.76;
95% CI 1.03–3.01; P=0.036; median, 20.5 vs 16 months) compared with
EGFR-TKI monotherapy, but no difference in overall survival (OS) was observed
between these two groups (HR, 1.52; 95% CI 0.81–2.83; P =0.19; median, 36
vs 29 months). However, patients who received the combination of
chemotherapy and EGFR-TKIs had longer PFS (HR, 2.78; 95% CI 1.57–4.93; P <0.0001;
median, 20.5 vs 12 months) as well as OS (HR, 2.86; 95% CI
1.56–5.27; P =0.001;
median, 36 vs 18 months) than those who received chemotherapy alone. Toxicities
were mild among the three treatment groups. Rash and diarrhea were common
adverse events (AEs) in the EGFR-TKI group, anemia and nausea in the
chemotherapy group, and anemia and diarrhea in the combination group.
Conclusion: This
study demonstrated that the combination of chemotherapy with EGFR-TKIs as
first-line treatment has a significant effect on PFS in patients with advanced
NSCLC whose tumors harbor activating EGFR mutations. The combination treatment
had more toxicity, but was clinically manageable.
Keywords: non-small-cell
lung cancer, epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
chemotherapy, adjuvant therapy, retrospective study