110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

阿魏酸通过抑制 TGF-β/Smadsignaling 通路减弱肝纤维化和肝星状细胞活化
Authors Mu M, Zuo S, Wu RM, Deng KS, Lu S, Zhu JJ, Zou GL, Yang J, Cheng ML, Zhao XK
Received 6 September 2018
Accepted for publication 31 October 2018
Published 3 December 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4107—4115
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S186726
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Purpose: Liver fibrosis
is a worldwide health issue. Development of effective new drugs for treatment
of this disease is of great importance. This study investigated the therapeutic
effects of ferulic acid on liver fibrosis in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and methods: Human
hepatic stellate cell line (HSC) LX-2 was used for in vitro assays.
Transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) was used to induce hepatic fibrosis in
LX-2 cells. Western blot was used to detect protein levels of collagen I,
fibronectin, α-smooth muscle actin (SMA), p-Smad2, p-Smad3, p-p38, and p-JNK.
Gene expression was measured by RT-qPCR. Fluorescence staining was used to
determine localization of Smad4. CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in SD rats was
used as an in vivo model. Histological features were detected by
hematoxylin and eosin staining. Levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT),
aspartate aminotransferase (AST), hexadecenoic acid (HA), and hydroxyproline
(Hyp) were measured by ELISA.
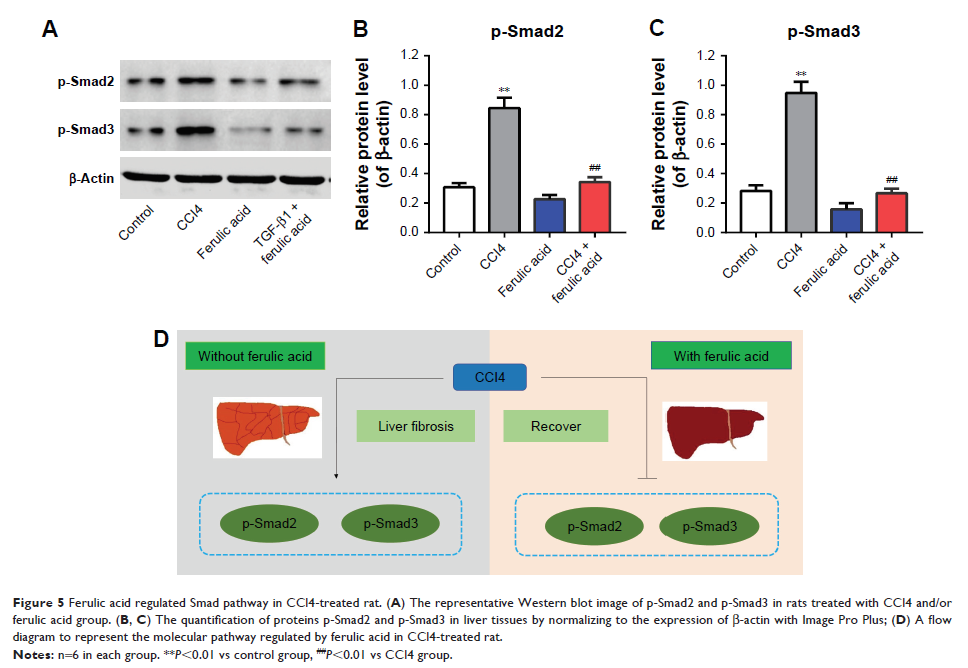
Results: TGF-β1
treatment significantly increased levels of collagen I, fibronectin, α-SMA,
p-Smad2, p-Smad3, and Smad4 in LX-2 cells. Ferulic acid improved TGF-β1-induced
hepatic fibrosis via regulation of the TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Consistent with
in vitro data, CCl4 caused severe hepatic fibrosis in SD rats, as
determined by ALT, AST, HA, and Hyp upregulation. Protein levels of p-Smad2 and
p-Smad3 in liver tissues were significantly increased following treatment with
CCl4. All CCL4-induced changes were markedly attenuated by ferulic acid
treatment.
Conclusion: Ferulic acid
potently improved hepatic fibrosis via inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad pathway
in vitro and in vivo. These findings provided evidence for potential
use of ferulic acid to treat or prevent liver fibrosis.
Keywords: ferulic
acid, TGF-β1, CCl4, hepatic fibrosis, Smad signaling pathway