110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素通过靶向大鼠中的 mTOR 通路减轻类风湿性关节炎诱导的炎症和滑膜增生
Authors Dai QD, Zhou D, Xu LP, Song XW
Received 30 May 2018
Accepted for publication 31 October 2018
Published 3 December 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4095—4105
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S175763
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Purpose: Rheumatoid
arthritis (RA) is a chronic, progressive autoimmune disease characterized by
aggressive and symmetric polyarthritis. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)
was reported to be a new target for RA therapy and its inhibitor rapamycin can
significantly reduce the invasive force of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Here,
we determined the effect of curcumin to alleviate inflammation and synovial
hyperplasia for the therapy of RA.
Materials and methods: Collagen-induced
arthritis (CIA) was developed in Wistar rats and used as a model resembling RA
in humans. Rats were treated with curcumin (200 mg/kg) and the mTOR
inhibitor rapamycin (2.5 mg/kg) daily for 3 weeks. Effects of the treatment on
local joint, peripheral blood, and synovial hyperplasia in the pathogenesis of
CIA were analyzed.
Results: Curcumin and
rapamycin significantly inhibited the redness and swelling of ankles and joints
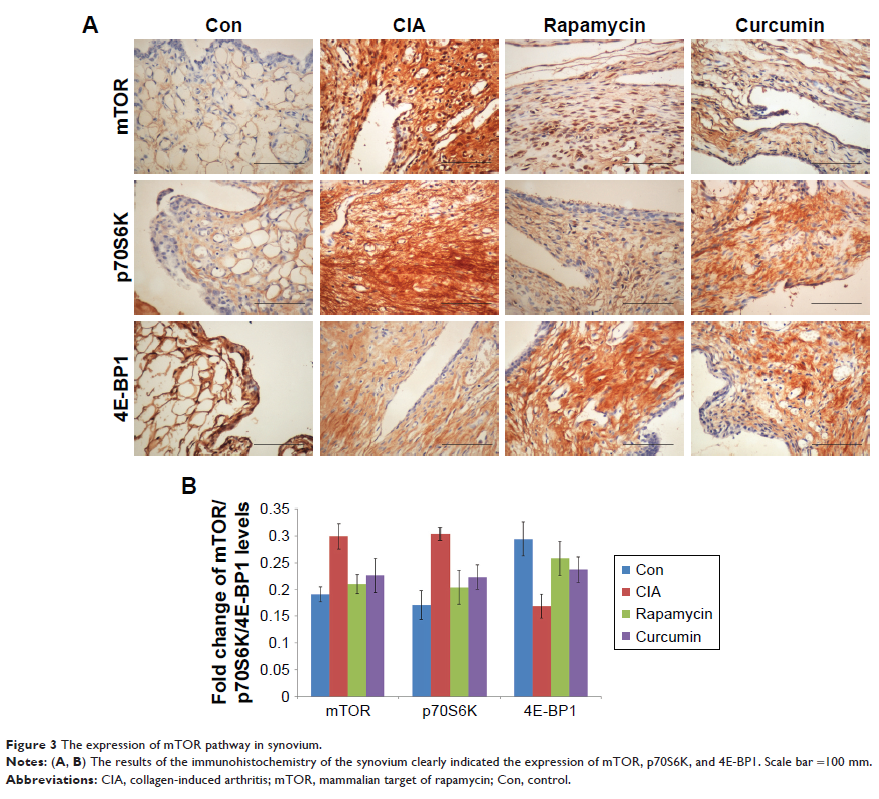
in RA rats. Curcumin inhibited the CIA-induced mTOR pathway and the RA-induced
infiltration of inflammatory cells into the synovium. Curcumin and rapamycin
treatment inhibited the increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines including
IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-1, and MMP-3 in CIA rats.
Conclusion: Our findings
show that curcumin alleviates CIA-induced inflammation, synovial hyperplasia,
and the other main features involved in the pathogenesis of CIA via the mTOR
pathway. These results provide evidence for the anti-arthritic properties of
curcumin and corroborate its potential use for the treatment of RA.
Keywords: rheumatoid
arthritis, curcumin, rapamycin, mammalian target of rapamycin, collagen-induced
arthritis