110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-411 通过调节 ZnT1 抑制膀胱癌的发展
Authors Liu Y, Liu T, Jin H, Yin L, Yu H, Bi J
Received 10 May 2018
Accepted for publication 3 September 2018
Published 4 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8695—8704
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S173750
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: At
present, the molecular genetics of the development and progression of bladder
cancer are still unclear. In recent years, the pathological relevance and
significance of microRNAs (miRNAs) in bladder cancer have attracted increasing
attention.
Methods: The
expressions of miR-411 and zinc transporter 1 (ZnT1) in bladder cancer were
determined by western blot and real-time PCR. Biological software, luciferase
reporter gene, Western blot and real-time PCR were used to determine the
regulatory effect of miR-411 on ZnT1. MTT and transwell were used to confirm
the regulatory effect of miR-411 on bladder cancer cells. MTT and transwell
were used to find how miR-411 modulated the biological activity of bladder
cancer cells by regulating ZnT1.
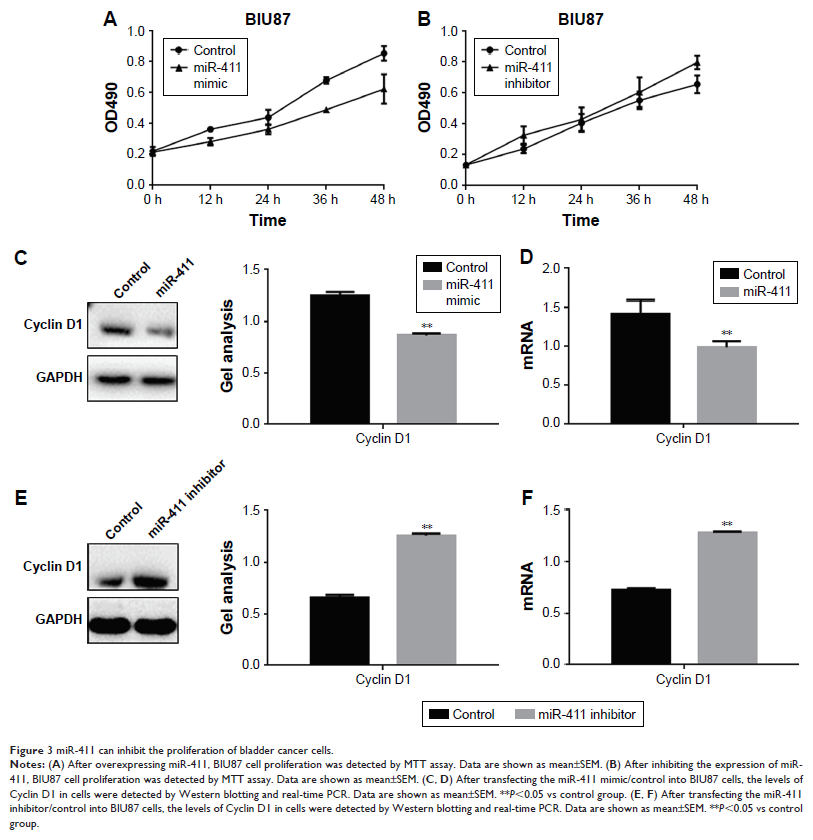
Results: The
expression of miR-411 was low in bladder cancer and was negatively correlated
with ZnT1. MiR-411 can inhibit the activity and the expression of ZnT1. MiR-411
can inhibit the growth and metastasis of bladder cancer cells. MiR-411
inhibited the growth and metastasis of bladder cancer cells by targeting
ZnT1.
Conclusion: The
miR-411 target ZnT1 may provide a potential therapeutic target for the
treatment of bladder cancer.
Keywords: miR-411,
ZnT1, bladder cancer, proliferation, metastasis