110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

N-乙酰半胱氨酸酰胺通过 Nrf2-ARE 通路在创伤性脑损伤小鼠模型中提供神经保护作用
Authors Zhou Y, Wang HD, Zhou XM, Fang J, Zhu L, Ding K
Received 5 July 2018
Accepted for publication 16 October 2018
Published 4 December 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4117—4127
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S179227
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: Increasing
evidence demonstrate N-acetylcysteine amide (NACA) provides neuroprotection and
attenuated oxidative stress in rats following traumatic brain injury (TBI). The
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)–antioxidant response element
(ARE) signal pathway is activated after TBI and provides a protective effect
against TBI. However, the function and mechanism of NACA in mice after TBI
remain unknown. This study was to evaluate the neuroprotection of NACA and the
potential action of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in a weight-drop mouse model of TBI.
Materials and methods: Four
groups of animals were randomly divided into sham, TBI, TBI+vehicle, and
TBI+NACA (100 mg/kg, administered intraperitoneally). The protein levels of
Nrf2, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), NAD(P)H: quinine oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1),
cleaved caspase-3 and the mRNA levels of HO-1 and NQO1 were detected. The
neurobehavior, neuronal degeneration, apoptosis and oxidative stress were also
assessed.
Results: Treatment
with NACA significantly improved neurologic status at days 1 and 3 following
TBI. Moreover, NACA promoted Nrf2 activation a day after TBI. The protein and
mRNA levels of HO-1 and NQO1 were upregulated by NACA. Meanwhile, NACA
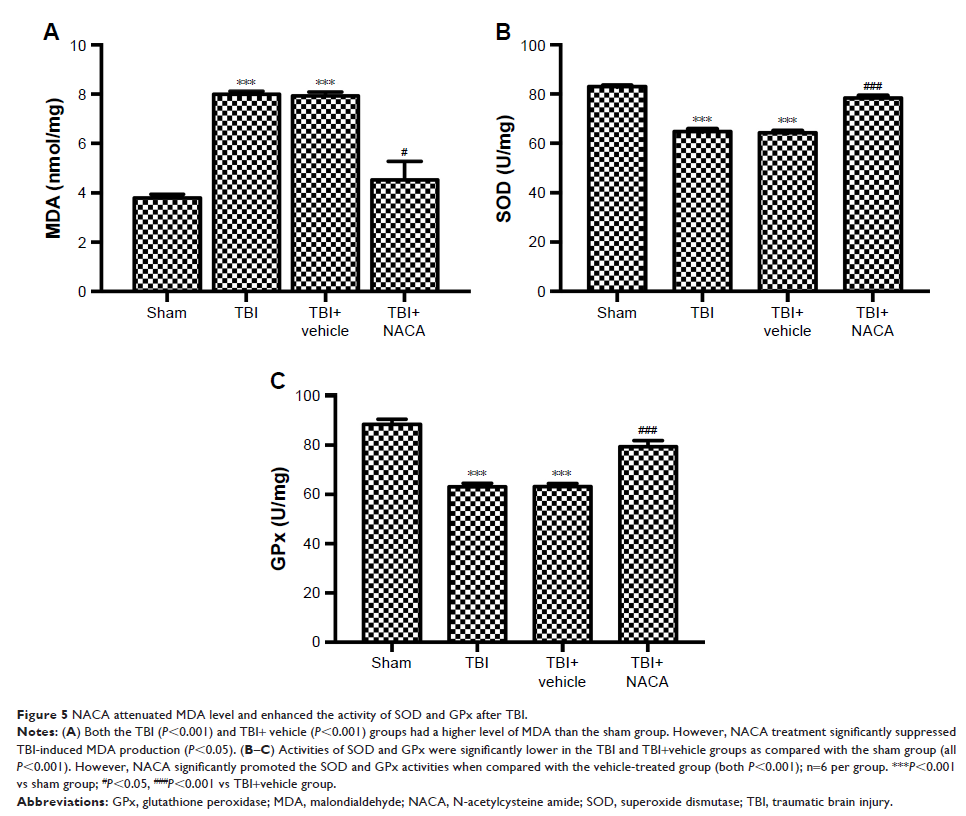
treatment significantly reduced the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) and enhanced
the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx),
which indicated NACA attenuated oxidative stress following TBI. NACA
prominently reduced the protein level of cleaved caspase-3 and TUNEL-positive
cells, indicating its antiapoptotic effect. Additionally, Fluoro-Jade C
staining showed NACA alleviated neuronal degeneration a day after TBI.
Conclusions: Our study
reveals that NACA potentially provides neuroprotection via the activation of
the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway after TBI in mice.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine
amide, traumatic brain injury, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2,
heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), NAD(P)H: quinine oxidoreductase-1, oxidative stress