110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于细菌磁小体的纳米载体用于体外共同递送癌症治疗剂
Authors Long R, Dai Q, Zhou X, Cai D, Hong Y, Wang SB, Liu Y
Received 27 July 2018
Accepted for publication 6 November 2018
Published 4 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 8269—8279
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S180503
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Abstract: In recent
times, co-delivery of therapeutics has emerged as a promising strategy for
treating dreadful diseases such as cancer.
Materials and methods: In this
study, we developed a novel nanocarrier based on bacterial magnetosomes (BMs)
that co-loaded with siRNA and doxorubicin (DOX) using polyethyleneimine (PEI)
as a cross-linker (BMs/DP/siRNA). The delivery efficiency of siRNA as well as
the pH-responsive release of DOX, and synergistic efficacy of these
therapeutics in vitro were systematically investigated.
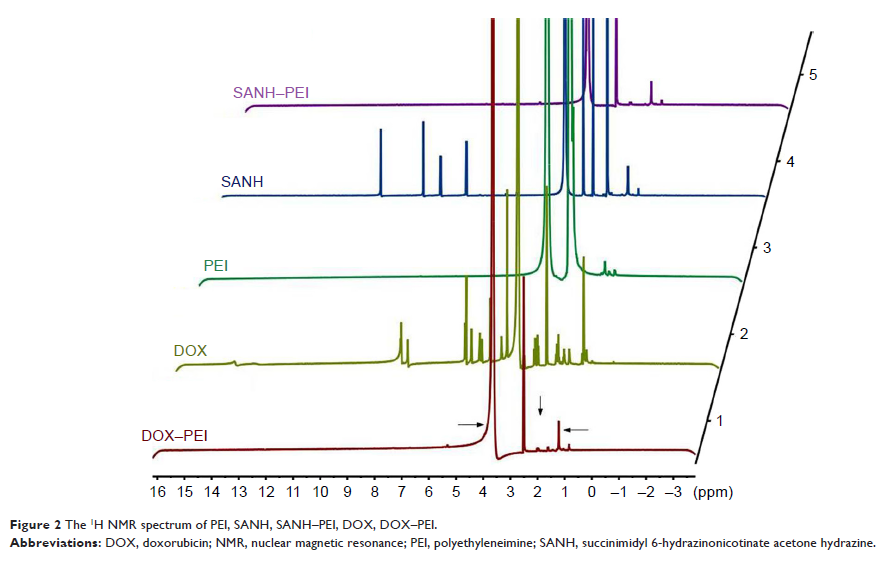
Results: The
structure of DOX–PEI (DP) conjugates that synthesized via hydrazone bond
formation was confirmed by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The
in vitro release experiments showed that the DP conjugate (DOX-loading
efficiency – 5.77%±0.08%) exhibited the long-term release behavior.
Furthermore, the optimal BMs/DP/siRNA particle size of 107.2 nm and the
zeta potential value of 31.1±1.0 mV facilitated enhanced cellular
internalization efficiency. Moreover, the agarose gel electrophoresis showed
that the co-delivery system could protect siRNA from degradation in serum and
RNase A. In addition, the cytotoxicity assay showed that BMs/DP/siRNA could
achieve an excellent synergistic effect compared to that of siRNA delivery
alone. The acridine orange (AO)/ethidium bromide (EB) double staining assay
also showed that BMs/DP/siRNA complex could induce cells in a stage of late
apoptosis and nanocomplex located in the proximity of the nucleus.
Conclusion: The combination
of gene and chemotherapeutic drug using BMs is highly efficient, and the
BMs/DP/siRNA would be a promising therapeutic strategy for the future
therapeutics.
Keywords: bacterial
magnetosomes, co-delivery, gene therapy, pH-responsive release