110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

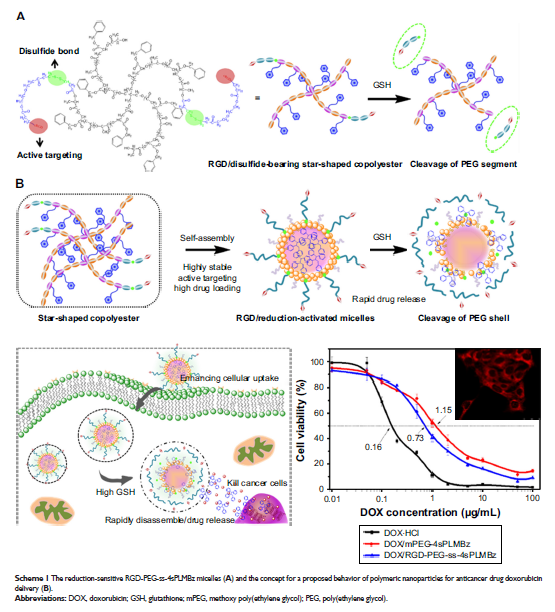
高度稳定的 RGD/二硫键桥式星形生物可降解纳米载体,用于提高载药效率、快速细胞摄取和按需货物释放
Authors Yan J, Zhang H, Cheng F, He Y, Su T, Zhang X, Zhang M, Zhu Y, Li C, Cao J, He B
Received 12 July 2018
Accepted for publication 22 October 2018
Published 4 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 8247—8268
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S179906
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Stability, enhanced drug-loading
efficiency (DLE), and specific accumulation of therapeutics at tumor sites
remain major challenges for successful cancer therapy.
Purpose: This
study describes a newly developed intelligent nanosystem that integrates
stealthy, active targeting, stimulus-responsiveness, and π-π interaction
properties in a single carrier, based on the multifunctional star-shaped
biodegradable polyester.
Patients and methods: This highly stable, smart nanocarrier with spherical
structures and a low critical micelle concentration (CMC) can provide spacious
harbor and strong π–π interaction and hydrophobic interactions for hydrophobic
doxorubicin (DOX). Its structure and morphology were characterized by proton
nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) spectra, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR)
spectra, Gel permeation chromatography (GPC), dynamic light scattering (DLS),
scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Antitumor effciency of polymeric micelles using CCK-8 assay, and the
intracellular-activated delivery system was tracked by confocal laser scanning
microscopy (CLSM) and flow cytometry.
Results: The
synthesized copolymer can be self-assembled into nanoparticles with size of 50
nm and critical micellar concentration of 2.10 µg/mL. The drug-loading content
of nanoparticles can be enhanced to 17.35%. Additionally, the
stimulus-responsive evaluation and drug release study showed that the
nanocarrier can rapidly respond to the intracellular reductive environment and
dissociate for drug release. An in vitro study demonstrated that the
nanocarrier can ferry doxorubicin selectively into tumor tissue, rapidly enter
cancer cells, and controllably release its payload in response to an
intracellular reductive environment, resulting in excellent antitumor activity
in vitro.
Conclusion: This
study provides a facile and versatile approach for the design of
multifunctional star-shaped biodegradable polyester nanovehicles for effective
cancer treatment.
Keywords: intelligent,
star-shaped, biodegradable multifunctional polyester, stimuli-responsiveness,
intracellular drug delivery, active targeting, cancer therapy