110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

NELFCD 的过表达促进结肠直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Song S, Li D, Yang C, Yan P, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Hu G, Lin C, Li X
Received 3 September 2018
Accepted for publication 30 October 2018
Published 5 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8741—8750
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S186266
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Purpose: Negative
elongation factor complex member C/D (NELFCD), mapped to chromosome 20q13.32,
has been found to be significantly overexpressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) by
our previous research. However, whether its overexpression contributes to CRC
development is unknown. We aimed to explore the biological and clinical roles
of NELFCD in CRC.
Materials and methods: The
expression of NELFCD was detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot. The biological
function of NELFCD on CRC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and
apoptosis was detected by cell counting kit-8, plate colony formation assay,
transwell migration and invasion assays, and flow cytometry in vitro and by
murine xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Moreover, we evaluated the correction
between its expression level and clinicopathologic parameters.
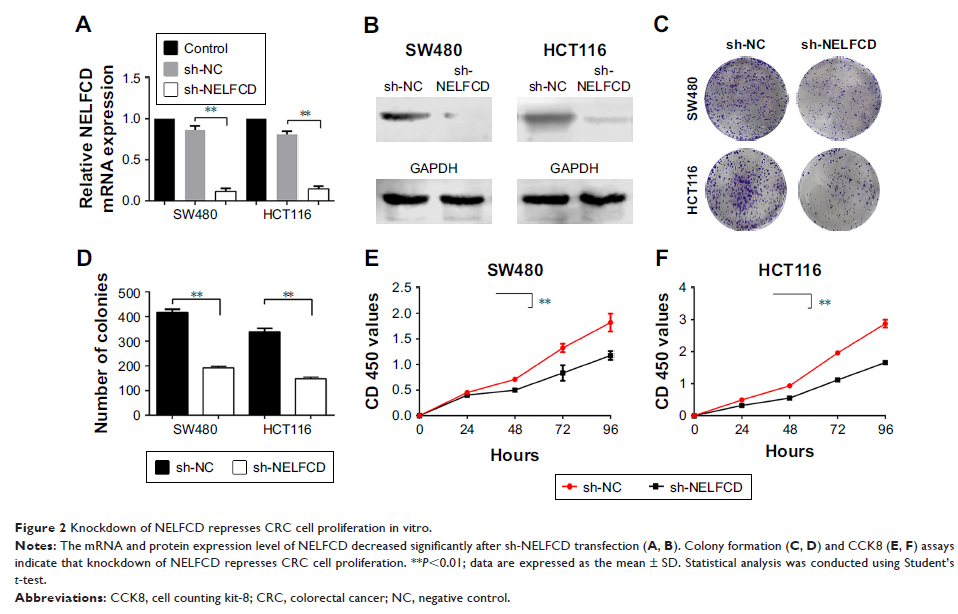
Results: We found
NELFCD was overexpressed in 50 pairs of CRC tissues in comparison to the
adjacent nontumor tissues (P <0.05). Knockdown of NELFCD significantly impaired
cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities, facilitated cell
apoptosis in vitro, and inhibited tumorigenesis of CRC cells in vivo. NELFCD
levels were remarkably connected with tumor location in CRC patients.
Conclusion: NELFCD is
overexpressed and plays an oncogenic role in CRC. Targeting NELFCD may provide
a potential therapeutic option for NELFCD-amplified tumors.
Keywords: NELFCD,
colorectal carcinoma, CRC, oncogene