110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

总淋巴细胞计数、中性粒细胞-淋巴细胞比例和血小板-淋巴细胞比例作为晚期非小细胞肺癌放化疗的预后因素
Authors Song X, Chen D, Yuan M, Wang H, Wang Z
Received 24 September 2018
Accepted for publication 8 November 2018
Published 5 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6677—6683
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S188578
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Objective: The objective
of this study was to investigate the prognostic significance and the efficacy
evaluation of total lymphocyte count (TLC), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
(NLR), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in advanced non–small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with chemoradiotherapy.
Patients and methods: A total
of 389 advanced NSCLC patients who received chemoradiotherapy from 2011 to 2016
were enrolled in this retrospective study. TLC, NLR, and PLR were analyzed with
overall survival (OS). Survival data were identified with the Kaplan–Meier
method and optimal cutoff values with receiver operating characteristic curves.
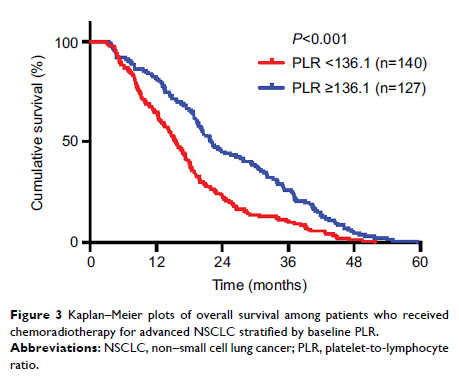
Results: The
median OS for all patients was 18.37 months. Pretreatment and median baseline
TLC was 2.47×103/μL (±0.78); NLR, 3.15 (±3.96); and PLR, 143.82
(±91.77); corresponding cutoffs were 2.4, 3.4, and 136.1. Higher TLC was
associated with superior median OS (21.78 vs 15.66 months, P <0.001), and
higher NLR and PLR with worse median OS (NLR: 14.13 vs 23.8 months, P <0.001; PLR:
15.49 vs 22.04 months, P <0.001).
Conclusion: The lymphopenia
indicators (TLC, NLR, and PLR) were significant prognostic indicators of
survival in advanced NSCLC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy.
Keywords: TLC, NLR,
PLR, advanced NSCLC, chemoradiotherapy