110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

眼科冻干环孢菌素聚合物胶束的稳定性、安全性和角膜动力学研究
Authors Shen Y, Yu Y, Chaurasiya B, Li X, Xu Y, Webster TJ, Tu J, Sun R
Received 10 May 2018
Accepted for publication 25 September 2018
Published 5 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 8281—8296
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S173691
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Carlos Rinaldi
Introduction: Cyclosporine-A
(CsA) is generally used as an immunosuppressant and is also prescribed for some
ophthalmic applications such as vernal keratoconjunctivitis and dry eye.
However, it is limited clinically due to its low aqueous solubility and ocular
bioavailability.
Methods: In this work,
lyophilized methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactide) (mPEG-PLA) polymer
micelles were prepared for ophthalmic formulations as a promising nano-carrier
for hydrophobic drugs like CsA. A mPEG-PLA diblock polymer was synthesized by
ring opening polymerization and CsA was loaded into mPEG-PLA micelles by a
simple film dispersion method. A uniform design of experiments was utilized to
optimize the final formulation. The obtained formulation was characterized for
diameter (57.0±3.2 nm), entrapment efficiency % (98.51±1.4), and in vitro
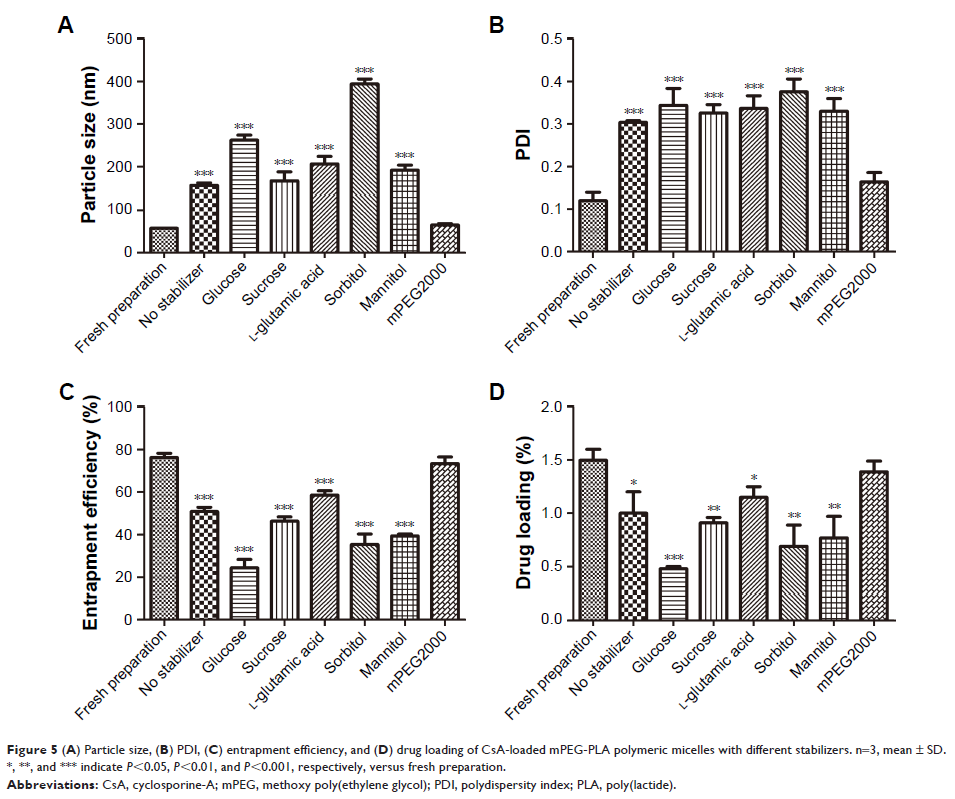
release. Moreover, incorporating the stabilizer mPEG2000 could increase the in
vitro stability of the lyophilized CsA-loaded mPEG-PLA micelles.
Results: Results showed
a sustained release of CsA from the micelles. Drug concentration and
time-dependent cytotoxicity of human corneal epithelial-2 cells was observed.
Additionally, the transcorneal mechanism of mPEG-PLA micelles was studied and
the results showed that the mPEG-PLA micelles mainly absorbed by a paracellular
pathway via corneal epithelial cells.
Conclusion: Taken together,
the results proved that this mPEG-PLA diblock polymer can be potentially used
as a nanoscopic carrier to deliver hydrophobic drugs in a controlled manner to
the ocular region and, thus, deserves further attention.
Keywords: CsA, mPEG-PLA
micelles, lyophilization, physicochemical characteristics, transcorneal
mechanism