110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

云南升麻中提取的环菠萝烷型三萜衍生物对三阴性乳腺癌细胞的抗癌效果
Authors Li X, Wang W, Fan Y, Wei Y, Yu LQ, Wei JF, Wang YF
Received 26 August 2018
Accepted for publication 25 October 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 6715—6729
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S185387
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: The roots
and rhizomes of Cimicifuga yunnanensis Hsiao are commonly used as
anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic remedies and detoxification
agents in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Although C. yunnanensis has
been considered as supplementary medicine for several disorders, the antitumor
effect of this herb and its key components has not been explored.
Materials and methods: The
rhizomes of C. yunnanensis were isolated by chromatographic
techniques. Structures of isolated compounds were identified based on
spectroscopic methods and comparison with published data. The in vitro
anticancer activities of purified components were also performed by MTT
experiments. The in vivo anticancer activities were examined by subcutaneous
tumor model or a breast cancer liver metastasis model.
Results: In this study,
we aimed to identify and characterize the effective antitumor components from
the rhizomes of C. yunnanensis . By bioassay-guided fractionation
techniques and chemical characterization, 12 cycloartane triterpenes and four
chromones were isolated, among them, 11 compounds were identified in this genus
at first. The identified two compounds showed dramatic inhibitory activities
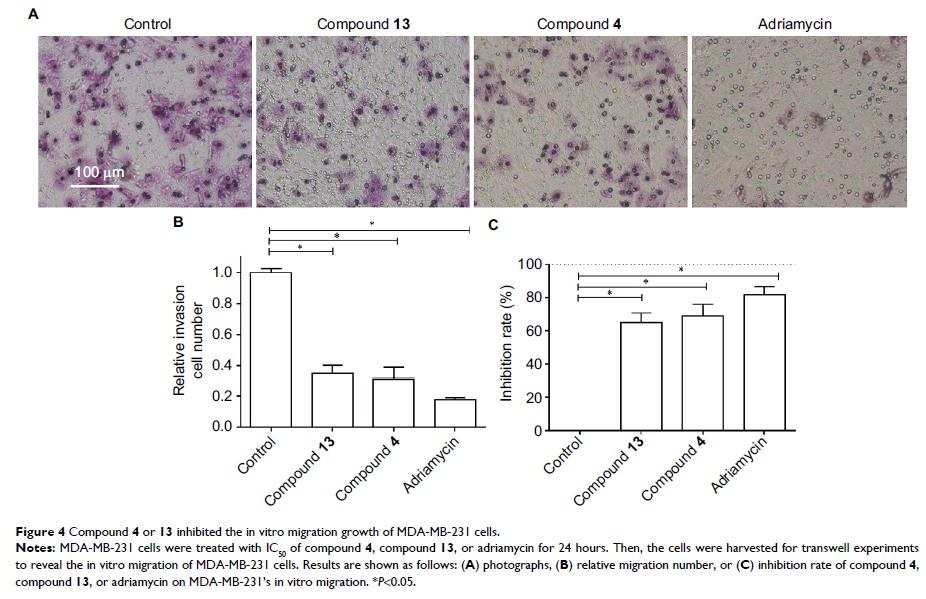
against breast cancer cells: compound 4 (23-epi-26-deoxyactein) and compound 13
(cimigenol). Then, we examined the antitumor effect of these two selective
candidate chemicals on triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells in vivo and
found that they could reduce tumor growth in subcutaneous tumor model or breast
cancer liver metastasis model.
Conclusion: These
results suggested that the selective compounds isolated from C. yunnanensis Hsiao
could be the promising new agents for TNBC treatment.
Keywords: Cimicifuga , Cimicifuga yunnanensis ,
cycloartane triterpenoids, anticancer activity, triple-negative breast cancer,
breast cancer liver metastasis