110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Salubrinal 通过 mHypoE-44 下丘脑神经元中的核因子活化 B 细胞 κ 轻链增强子途径消除棕榈酸诱导的瘦素抵抗和内质网应激
Authors Zhang M, Jiang X, Qu M, Gu H, Sha Q, Hua F
Received 6 July 2018
Accepted for publication 2 October 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 893—899
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S179346
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
Background: The prevalence
of obesity is growing rapidly and has become a global problem that increases
the risk for many diseases. It is influenced by many factors, including
consumption of the Western-style diet, characterized as a high-fat diet. Within
the central nervous system, the hypothalamus is a critical site in maintaining
energy homeostasis and sensing nutrient status, including palmitate, the major
component of high-fat-diet.
Methods: In the
present study, we conducted a variety of studies to investigate the specific
role of salubrinal on palmitate-induced hypothalamic cell death, leptin
signaling, and ER stress in an embryonic hypothalamic cell line. Experiments
were also performed to identify the underlying mechanisms of the protective
effect of salubrinal.
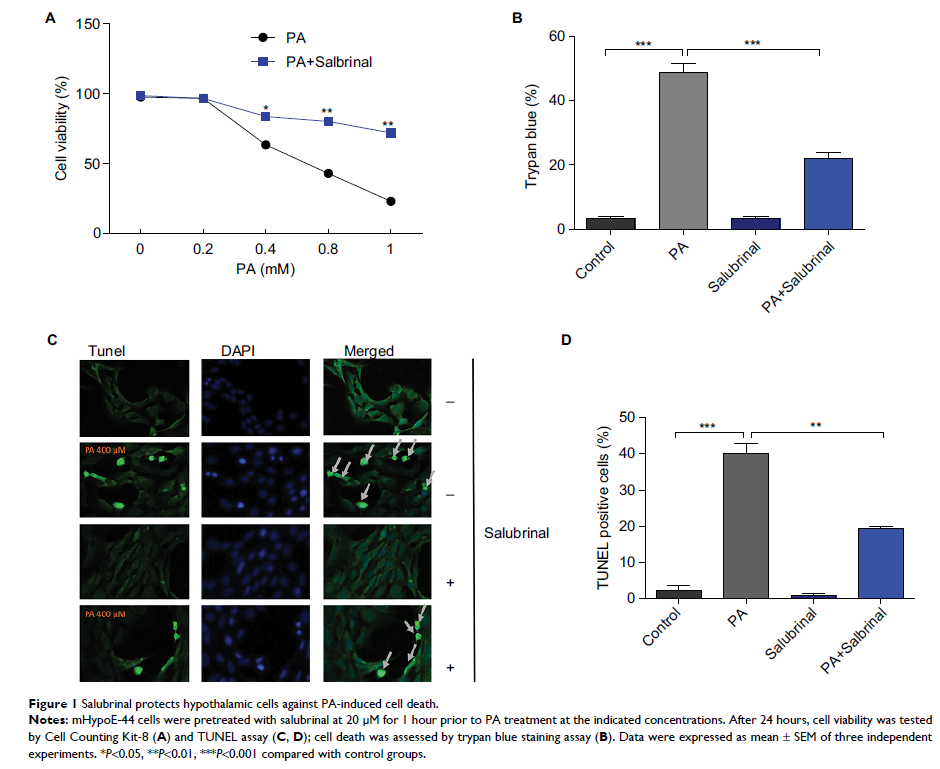
Results: Our results
indicate that salubrinal protects hypothalamic cells against PA-induced ER
stress and improves hypothalamic leptin sensitivity.
Conclusion: Taken
together, our findings conclusively reveal that salubrinal abrogates palmitate-induced
hypothalamic leptin resistance and ER stress via NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: obesity,
high-fat diet, palmitate, leptin resistance, ER stress, salubrinal