110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

切开诱导内固定治疗创伤性肢体骨折后血小板指数与深部手术部位感染的关系
Authors Zhang Z, Ji Y, Wang Z, Qiu X, Chen Y
Received 22 August 2018
Accepted for publication 9 November 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2533—2538
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S184877
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Objectives: Deep
surgical site infection (DSSI) is one of the most serious complications after
open induction internal fixation (ORIF) for traumatic limb fractures. In this
study, we aimed to investigate the diagnostic role of platelet indices
(platelet count [PLT], mean platelet volume [MPV], and platelet distribution
width [PDW]) in DSSI.
Patients and methods: Data obtained
between January 2011 and December 2017 in The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of
Nanjing University Medical School from cases (n=29) with DSSI and fracture
control subjects (n=29) matched for age, gender, and fracture type were
analyzed. The white blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil count, neutrophil
percentage, and platelet indices from blood samples were compared between case
and control groups. In addition, the cutoff value, sensitivity, and specificity
were calculated by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: No
significant differences were detected in demographic features, the WBC count,
neutrophil count, neutrophil percentage, and MPV values between two groups (P >0.05). The PLT
values were significantly higher in the case group than in the control group
(303.00±139.27 vs 196.10±59.61 [109/μL], P=0.001). The PDW
values of the case and control groups were 11.77±2.71 and 13.19±2.39%,
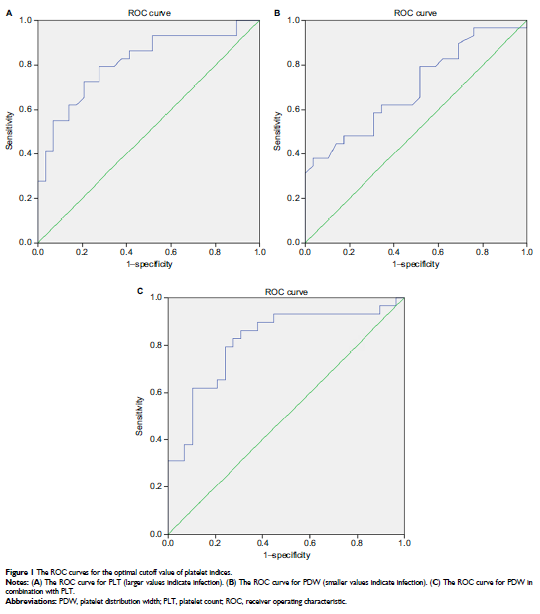
respectively, and were significantly lower in the case group (P =0.001). ROC curve
analysis suggested a cutoff point for PLT as 215.50 (109/μL, larger
values indicate pathology) for the diagnosis of DSSI with the sensitivity and
specificity of 79.3 and 72.4%, respectively. For PDW, the cutoff point was
10.35% (smaller values indicate patients) for the diagnosis of DSSI with the
sensitivity and specificity of 37.9 and 96.6%, respectively.
Conclusion: Our results
suggest that PDW combined with PLT can be used as an important additional test
for the diagnosis of DSSI after ORIF for traumatic limb fractures, thus
reducing the cost and loss of time.
Keywords: surgical site
infection, internal fracture fixation, fracture, platelet count, platelet
function test