110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

槲皮素通过 Smad 途径抑制由转化生长因子-β1 诱导的人视网膜色素上皮细胞上皮间充质转化
Authors Cai W, Yu D, Fan J, Liang X, Jin H, Liu C, Zhu M, Shen T, Zhang R, Hu W, Wei Q, Yu J
Received 28 August 2018
Accepted for publication 24 October 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 4149—4161
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S185618
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Purpose: The purpose of
this study was to evaluate the effect and mechanism of quercetin on
TGF-β1-induced retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell proliferation, migration,
and extracellular matrix secretion.
Materials and methods: Cell
counting kit-8, transwell, wound-healing assays, and ELISA were used to assess
viability, migration, and collagen I secretion, respectively. Western blot
analysis and qPCR were employed to detect mRNA and protein expression levels,
respectively.
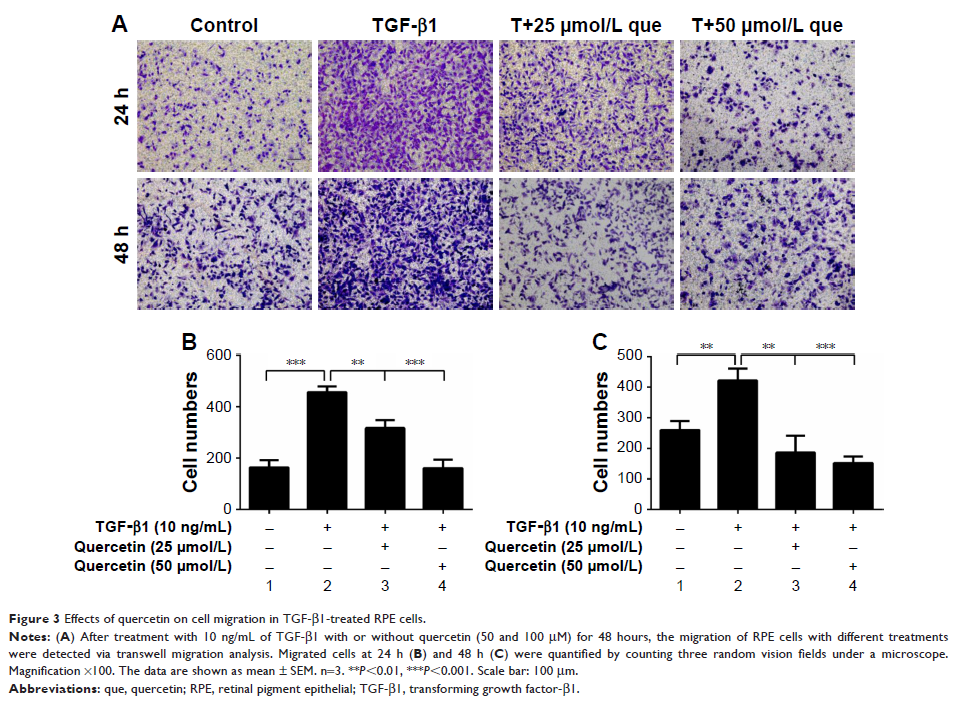
Results: Quercetin
suppressed TGF-β1-induced cell proliferation, migration, and collagen I
secretion. The results also showed that mRNA and protein expression of
epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related markers such as alpha-smooth
muscle actin and N-cadherin was downregulated by quercetin in TGF-β1-treated
RPE cells; conversely, quercetin upregulated the expression of E-cadherin and
tight junction protein 1 (ZO-1). In addition, quercetin could inhibit mRNA and
protein expression of matrix metalloproteinases. Quercetin may reverse the progression
of EMT via the Smad2/3 pathway.
Conclusion: Our
results demonstrate the protective effects of quercetin on RPE cell EMT,
revealing a potential therapeutic agent for proliferative vitreoretinopathy
treatment.
Keywords: proliferative
vitreoretinopathy, quercetin, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, transforming
growth factor-β1