110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

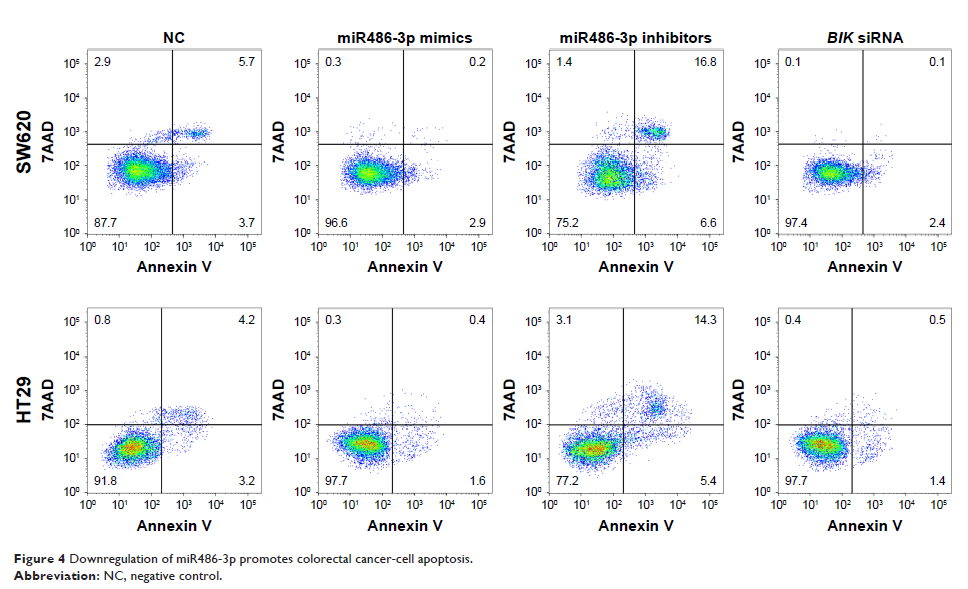
MicroRNA-486-3p 直接靶向 BIK 并调节结直肠癌细胞的凋亡和侵袭
Authors Feng L, Jing L, Han J, Wang G, Liu Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Wang F, Ma H, Liu Y
Received 16 July 2018
Accepted for publication 29 September 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8791—8801
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S180354
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background: MicroRNAs
influence almost every genetic pathway and are involved in colorectal cancer
(CRC). However, the biological role of miR486-3p in CRC remains to be
elucidated.
Methods: In this
study, miR486-3p expression in CRC cell lines and normal colonic epithelial
cells was determined. After miR486-3p mimic, inhibitor, and BIK siRNA
transfection, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration were examined.
Furthermore, the target of miR486-3p was identified by luciferase-reporter
assay and underlying molecular mechanisms studied.
Results: The
results revealed that miR486-3p was significantly upregulated in CRC compared
with normal colonic epithelial cells, whereas BIK expression was remarkably
downregulated in CRC cells. MTT assays demonstrated that suppression of
miR486-3p expression reduced CRC cell proliferation, whereas elevated miR486-3p
or BIK silencing induced cell proliferation. Wound-healing assays and transwell
experiments revealed that both upregulation of miR486-3p and downregulation of
BIK increased CRC cell migration and invasion ability. Moreover, bioinformatic
target prediction identified BIK as a putative target of miR486-3p. Knockdown
of miR486-3p was shown to upregulate BIK expression, whereas overexpression of
miR486-3p suppressed the expression of BIK. Luciferase reporter assay results
further confirmed this deduction.
Conclusion: In conclusion,
these findings suggest that miR486-3p is an oncogene in CRC. Gene therapy using
miR486-3p inhibition may provide a new clue for CRC therapy.
Keywords: colorectal
cancer, miR486-3p, BIK, apoptosis, invasion