110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

以转铁蛋白受体为靶向的 HMSN 可递送索拉非尼,用于难治性分化型甲状腺癌治疗
Authors Ke Y, Xiang C
Received 12 September 2018
Accepted for publication 6 November 2018
Published 6 December 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 8339—8354
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S187240
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Thyroid
cancer becomes the most common endocrine cancer with the greatest growing
incidence in this decade. Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor for the
treatment of progressive radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid
cancer (DTC), while the off-target toxicity effect is usually inconvenient for
patients taking.
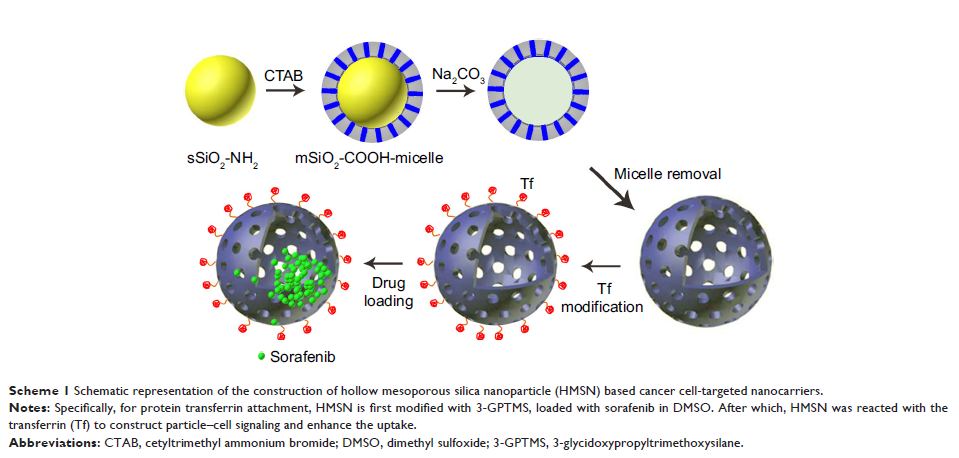
Methods: In this
study, hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) with transferrin
modification (Tf-HMSNs) were loaded with sorafenib (sora@Tf-HMSNs) to help
targeted delivery of sorafenib. Due to the biocompatible Tf shell, Tf-HMSNs
exhibited excellent biocompatibility and increased intracellular accumulation,
which improved the targeting capability to cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo.
Results: Sora@Tf-HMSNs
treatment exhibited the strongest inhibition effect of res-TPC-1 cells and
res-BCPAP cells compared with sora@HMSNs and sorafenib groups and induced more
cancer cell apoptosis. Finally, Western blot analysis was conducted to check
the expression of RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway after sorafenib encapsulated
Tf-HMSNs treatment.
Conclusion: Overall,
sora@Tf-HMSNs can significantly increase the effective drug concentration in
cancer cells and thus enhance the anticancer effect, which are expected to be
promising nanocarriers to deliver anticancer drugs for effective and safe
therapy for RAI-refractory DTC.
Keywords: sorafenib,
RAI-refractory DTC, hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles, transferrin,
RAF/MEK/ERK